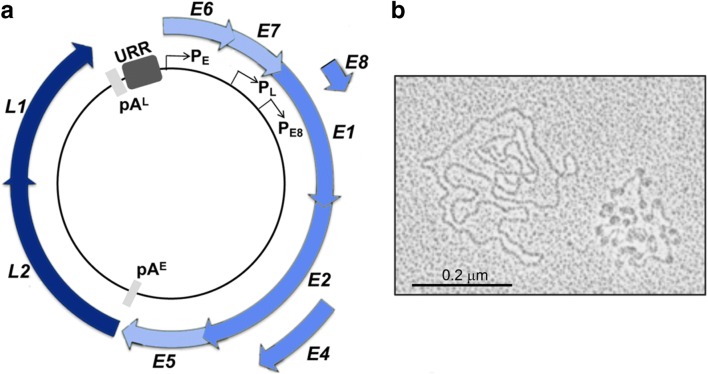
Fig. 1.
HPV genome organization. a The circular, double-stranded HPV genome is about 8000 base pairs and divided into three regions: the early, late and non-coding upstream regulatory region (URR). The early region contains open-reading frames (ORF), some overlapping of E1, E2, E4, E5, E6, E7 and E8. The late region contains L1 and L2 ORF—the capsid proteins. Viral transcription is controlled by the HPV E2 protein and host factors binding sequences within the URR. The main promoters are the early PE, the late PL and the E8 promoter PE8, and viral transcripts terminate at the early pAE or late pAL poly-adenylation sites. The URR also contains the origin of replication. b In a study in the late 1970s [3], electron microscopy of metal-shadowed HPV genomes isolated from plantar warts showed naked HPV DNA molecules (left) and nucleoprotein-DNA complexes (right) revealing an intricate ‘beads on a string’ conformation of nucleosomes. Reproduced with permission from the American Society for Microbiology