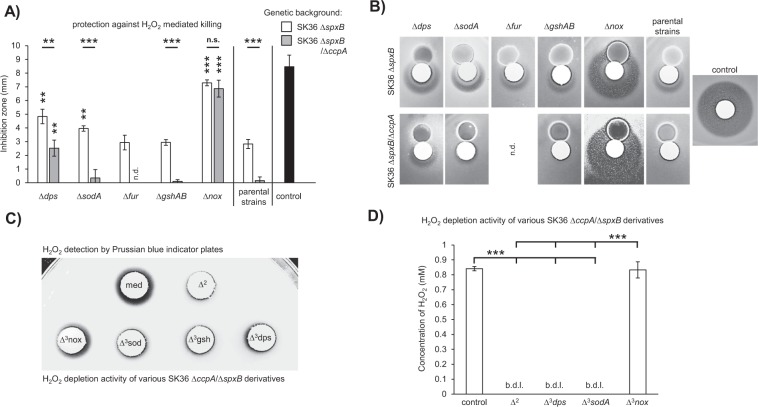
Fig. 6. Genes related to the protective effect.
H2O2 protection assays were performed with the indicated mutants and controls. a Mutations of dps, sodA, fur, gshAB, and nox were tested in the SK36 ΔspxB background, while dps, sodA, gshAB, and nox mutations were assayed in the SK36 ΔccpA/ΔspxB background. Paired t-tests were performed for each mutant relative to its parental stain. The respective significance levels are indicated by asterisks above each column. Significance levels between mutants of a respective gene in the SK36 ΔspxB and SK36 ΔccpA/ΔspxB backgrounds were tested with unpaired t-tests and are indicated above each pair of columns. b Representative examples of the inhibition zones for each tested mutant are presented. c, d Conditioned medium extracts of the SK36 ccpA/spxB double mutant, its derivatives (as indicated), and BHI (control) were tested in an H2O2 depletion assay. Initial H2O2 concentrations were 20 mM (c) and 1 mM (d). c Filter discs were soaked with the extract/H2O2 mixture and placed on Prussian-blue-indicator plates. The sizes of the resulting halos are proportional to the amount of H2O2 present. A representative image is shown. d H2O2 concentrations were determined with the Amplex Red Peroxide/Peroxidase Assay. Averages and standard deviations from at least three independent experiments are presented. Significance levels: **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n.d. not determined, n.s. not significant, b.d.l. below detection limit, med medium control, Δ2—SK36 ΔccpA/ΔspxB, Δ3nox—SK36 ΔccpA/ΔspxB/Δnox, Δ3sod—SK36 ΔccpA/ΔspxB/ΔsodA, Δ3gsh—SK36 ΔccpA/ΔspxB/ΔgshAB, Δ3dps—SK36 ΔccpA/ΔspxB/Δdps.