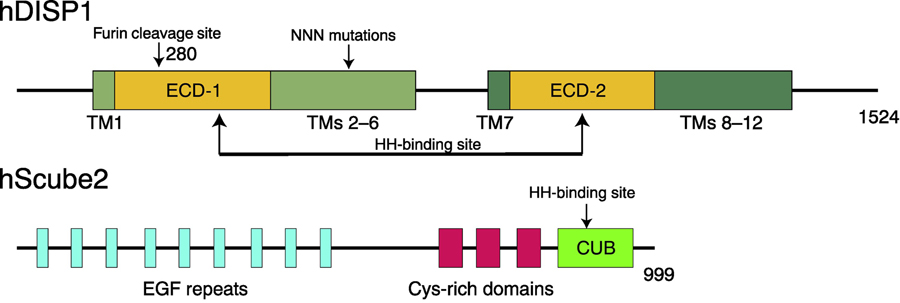
Figure 2. Secondary Structures of human DISP1 (hDISP1) and human Scube2 (hScube2).
DISP1 shares a similar structure with PTCH1, consisting of 12 TMs, two ECDs, and N-terminal and C-terminal cytosolic flexible regions. The ECDs are involved in HH-N binding (indicated by arrows). A proprotein convertase named Furin can cleave the ECD-I (cleavage site is labeled) of DISP1 triggering HH-N release. TMs 2–6 form an SSD and mutations in the SSD affect the release of HH-N. Scube2 protein works in the extracellular space and consists of 9 EGF-like repeats, three CRDs, and one CUB domain, which is essential for HH-N binding.