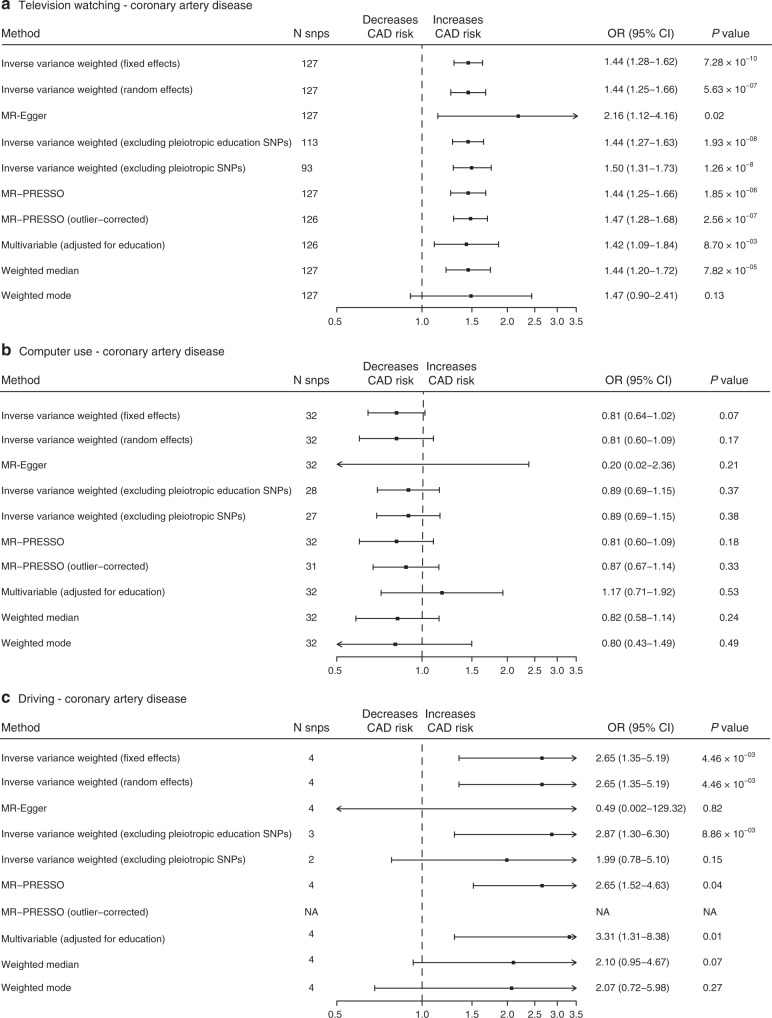
Fig. 3. Summary Mendelian randomization (MR) estimates of leisure sedentary behaviours on CAD.
Summary MR estimates of the causal association between (a) leisure television watching, (b) leisure computer use and (c) driving on coronary artery disease were derived from the main inverse-variance-weighted (MR-IVW), MR-Egger, MR-IVW excluding potentially pleiotropic single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) through education, MR-IVW excluding potentially pleiotropic SNPs through any trait, MR pleiotropy residual sum and outlier (MR-PRESSO), outlier-corrected MR-PRESSO, multivariable Mendelian randomization adjusted for educational years, weighted median and weighted mode-based estimator methods. On the X-axis, odds ratios are shown and data are represented as odds ratio and 95% confidence intervals. We considered two-sided P < 0.05 statistically significant, no adjustments were made for multiple testing. OR odds ratio, CI confidence interval.