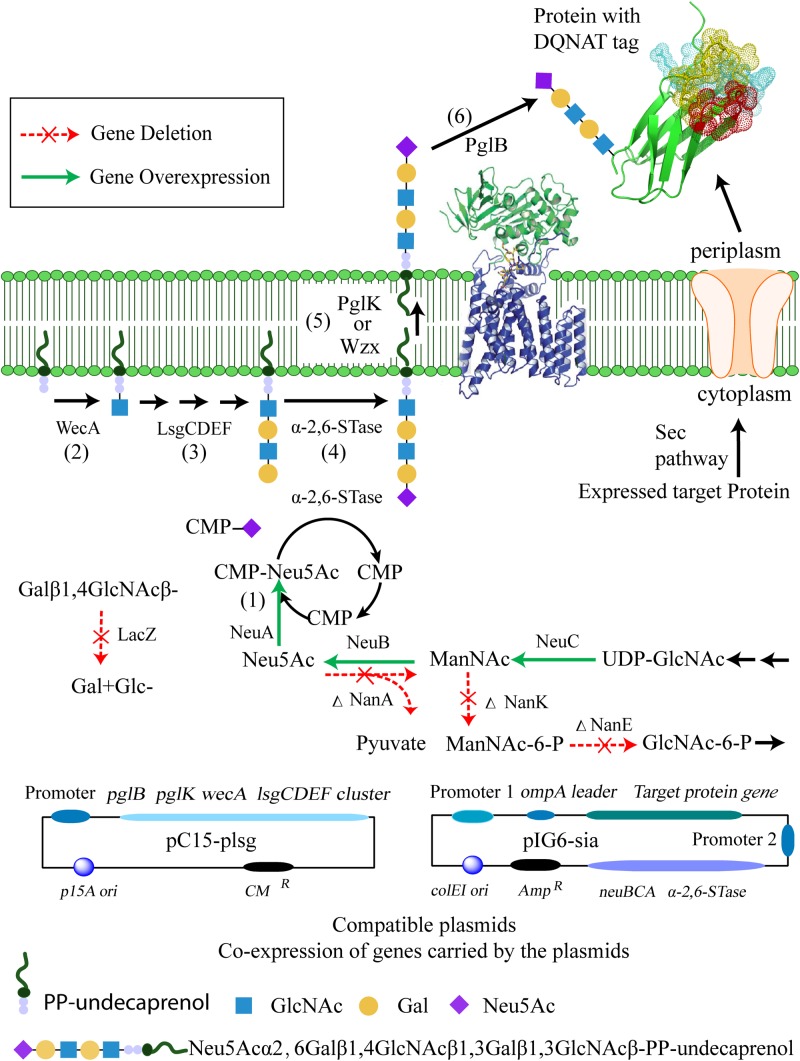
FIGURE 1.
The proposed biosynthetic pathway for the production of terminally sialylated proteins in the periplasm of E. coli, and associated plasmid constructs. Synthesis of CMP-Neu5Ac is achieved by the sub-pathway constructed with overexpressed neuBCA genes from C. jejuni (1). Synthesis of the pentasaccharide LLOs Gal-β-1,4-GlcNAc-β-1,3-Gal-β-1,3-GlcNAc-β-pp-undecaprenol and Neu5Ac-α-2,6-Gal-β-1,4-GlcNAc-β -1,3-Gal-β-1,3-GlcNAc- is achieved by the sub-pathway constructed with GlcNAc-1-phosphate glycosyltransferase (WecA) enzyme (2), glycosyltransferases (LsgCDEF) (3), and the α-2,6-STase (pl-ST6) enzyme (4). The sialylated glycan is flipped by PglK (or Wzx) flipases from the cytoplasmic to the periplasmic side of the membrane (5). The final modification of the target protein with the synthesized glycan is achieved by PglB (6).