FIGURE 2.
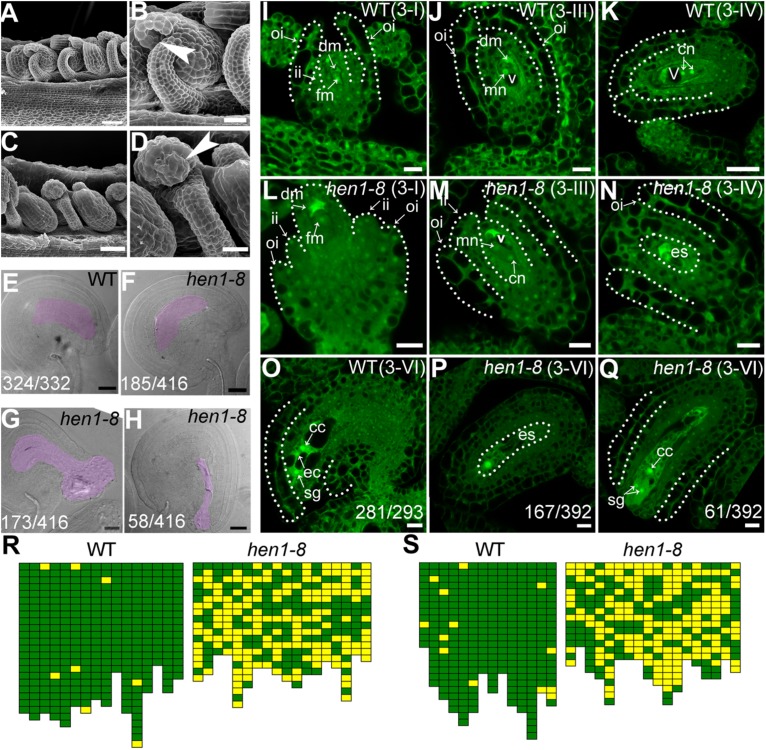
hen1-8 is defective in ovule development. (A–D) Scanning electron micrographs (SEMs) of mature ovules from wild type (A,B) or from hen1-8 (C,D). (B) and (D) are close-ups of (A) and (C), respectively. Arrows in (B,D) point at the micropyle. (E–H) Whole-mount ovule clearing of wild type (E) or hen1-8 (F–H). The ovule in (F) or in (G–H) represents normal or abnormal types, respectively. Embryo sacs are highlighted with lilac. (I–Q) Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) of wild-type (I–K,O) or hen1-8 (L–N,P,Q) ovules at stage 3-I (I,L), 3-III (J,M), 3-IV (K,N), or 3-VI (O–Q). Ovules were stained with PI and mid-optical sections are shown. For (I–Q), only hen1-8 ovules with visible nuclei were documented. For (E–H) and (O–Q), numbers on the bottom of each image indicate displayed ovules/total ovules examined. Cc, central cell; cn, chalazal nucleus; dm, degenerating megaspore; ec, egg cell; es, embryo sac; fm, functional megaspore; ii, inner integument; oi, outer integument; mn, micropylar nucleus; sg, synergid cell; v, vacuole. (R–S) Quantitative analysis of ovule development by ovule clearing (R) or by optical sections (S). Each pistil examined was represented by two neighboring columns; the number of cubes in each column indicates the number of countable ovules; normal and abnormal ovules (R) or embryo sacs (S) are displayed in green and yellow, respectively. Bars = 50 μm for (A,C); 20 μm for (B,D,E–H); 10 μm for (I–J,L–Q); 20 μm for (K).