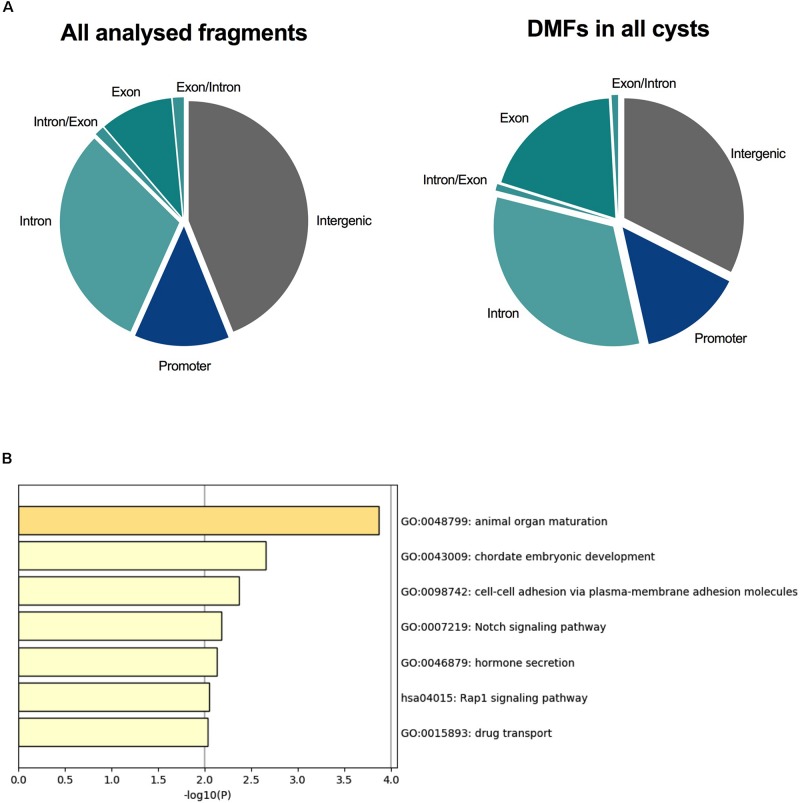
FIGURE 2.
All eight ADPKD cysts were differentially methylated across PKD-related pathways. (A) The proportion of fragments associated with each genomic element in the analysis. Intergenic fragments (both upstream and downstream of protein-coding genes) are gray. Promoter fragments are blue, and fragments within the gene body are shades of teal. Ninety-six DMFs were common in all eight cysts, with 54% of these occurring within the gene body. (B) Gene ontology identified common enriched pathways associated with these fragments. Animal organ maturation was the most significantly enriched, followed by embryonic development. Interestingly, cell-cell adhesion and Notch signaling, both associated with ADPKD, were also enriched in these differentially methylated fragments.