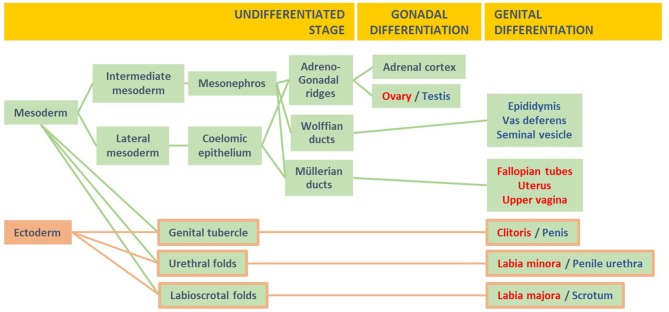
Figure 1.
The three stages of fetal sex differentiation. During the undifferentiated stage, the mesoderm gives rise to the adreno-gonadal primordia and the Wolffian and Müllerian ducts, whereas the ectoderm and mesoderm contribute to the formation of the genital tubercle and the urethral and labioscrotal folds. During the stage of gonadal differentiation, the testes or ovaries develop from the gonadal ridges. During the stage of genital differentiation, the internal and external genitalia differentiate along the male or the female pathway. Modified with permission from Rey et al. (7) © 2018 McGraw Hill Education.