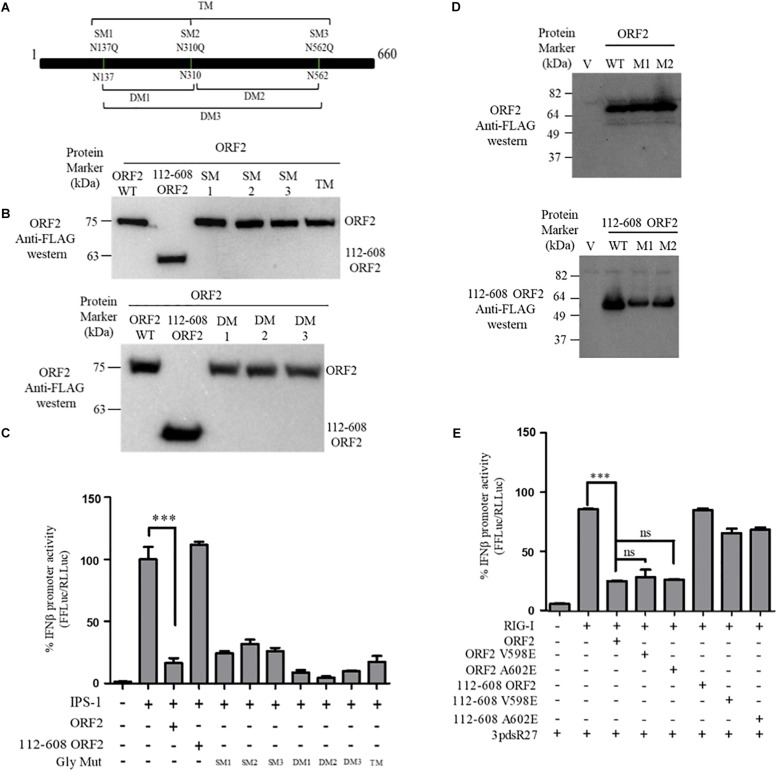
FIGURE 3.
ORF2 glycosylation and dimerization is not required for IFN-β inhibition: (A) A schematic showing the location of the three glycosylation sites and the mutations introduced in the FL ORF2. (B) Western blot analysis of WT and mutant FL ORF2 or 112-608 ORF2 in HEK293T cells. (C) For IPS-1 assay, 0.5 ng of IPS-1 was co-transfected with 25 ng of WT or mutant FL ORF2 or 112-608 ORF2 plasmids along with IFN-β firefly and TK Renilla luciferase reporter plasmids. Luciferase activity was measured 24 h post-induction. (D) Western blot analysis of the whole cell lysates of HEK293T cells expressing the WT FL ORF2 (top) or 112-608 ORF2 (bottom) and their two mutants, V598E (M1) and A602E (M2) ORF2. (E) RIG-I assay was performed with RIG-I (0.5 ng) and 25 ng of the WT and mutant ORF2 plasmids. Induction was given by transfecting 3pdsR27 24 h post-transfection. Luciferase activity was measured 16 h post-induction. Values are percent mean ± SD, n = 3 (∗∗∗ denotes p-values ≤ 0.001, ns denotes p-values ≥ 0.05).