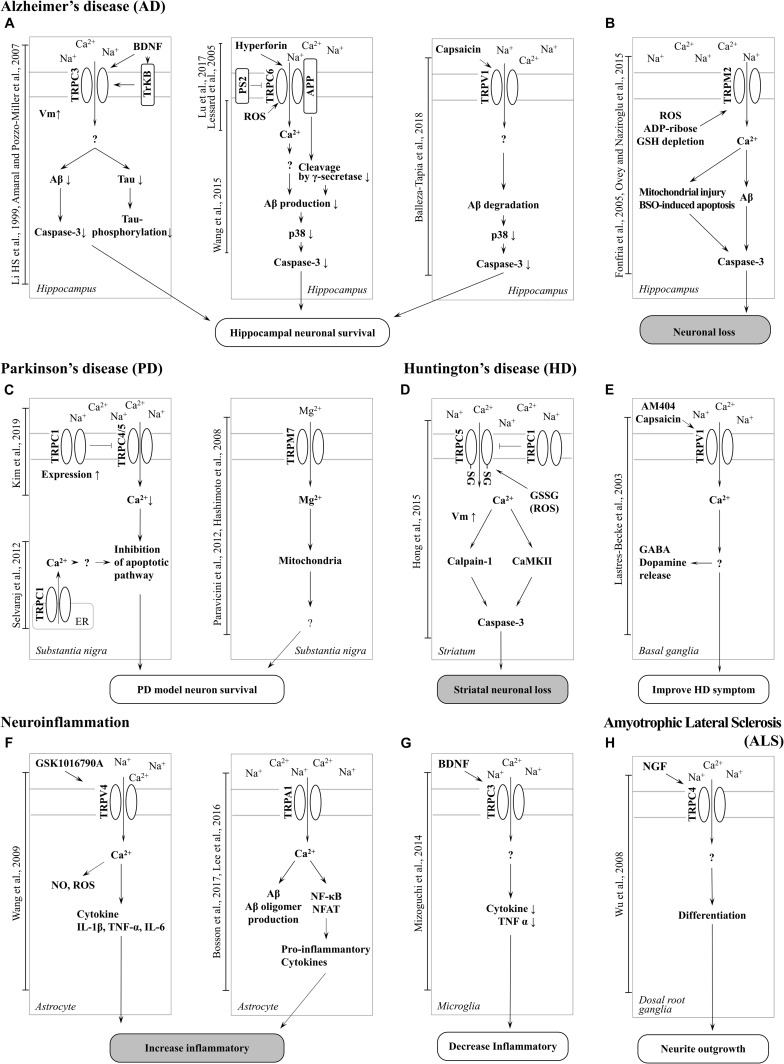
FIGURE 2.
Schematic of TRP channel-mediated mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases. (A) Activation of TRPC3, TRPC6 and TRPV1 channel increase neuronal survival in AD. (B) Neuronal loss can be induced by Aβ toxicity, ROS generation, and mitochondrial damage resulting from TRPM2 channel-mediated Ca2 + entry in AD. TRPA1 is also involved in neuroinflammation in AD. (C) Inhibition of TRPC4/5 by TRPC1 contribute to inhibition of apoptotic pathways and TRPM7-mediated Mg2 + influx is involved in neuronal survival in PD. (D) Increased activity of TRPC5 by oxidative stress induces striatal neuronal loss via Ca2 +-dependent pathways in HD. (E) Activation of TRPV1 by an agonist improves HD symptoms. (F) Activation of TRPV4 and TRPA1 induces a proinflammatory response in astrocytes (G) whereas upregulation of surface TRPC3 induced by BDNF regulates microglial functions and reduces inflammation. (H) Upregulation of TRPC4 promotes neurite outgrowth and differentiation in DRG (GTEx Consortium, 2013).