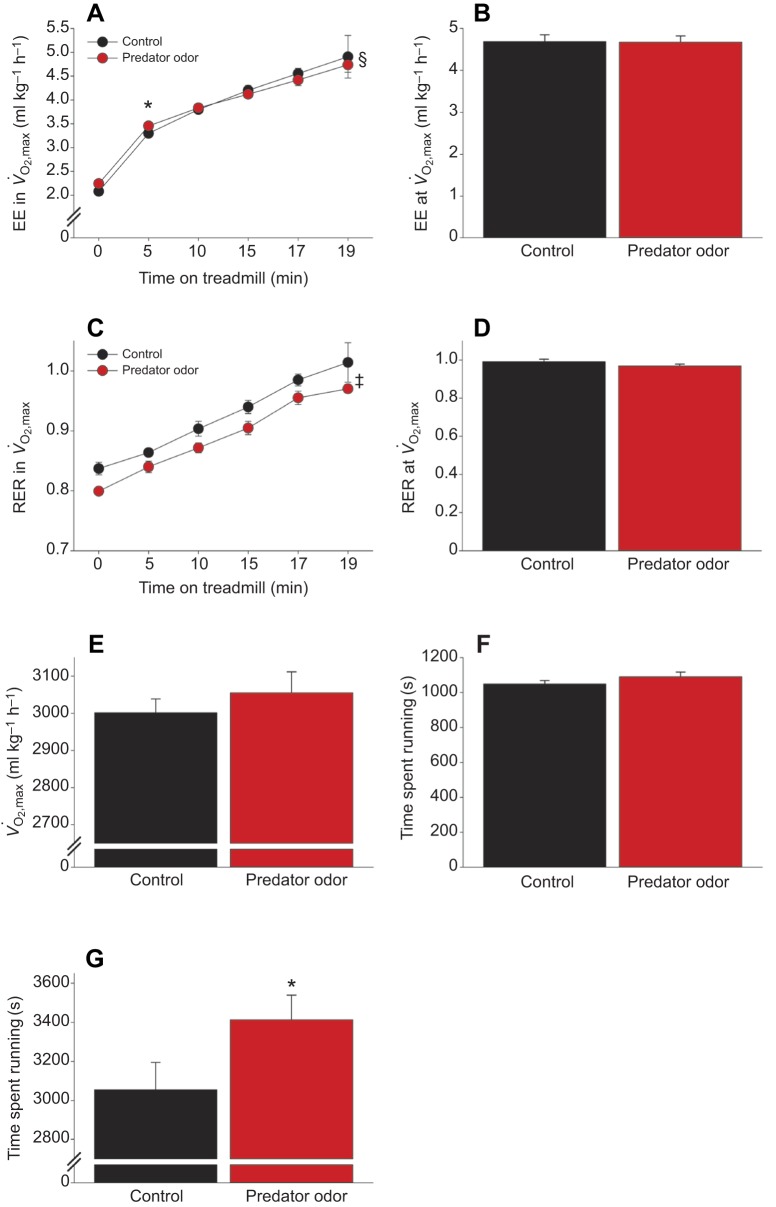
Fig. 5.
Acute predator odor exposure alters fatigue and fuel utilization without changing V̇O2,max. (A–F) During a V̇O2,max treadmill test, exposure to predator odor increased EE in the first 5 min of running (A) and decreased RER (C) without significantly altering maximal EE (B), RER (D), V̇O2 (E) or time spent running (F). (G) During a lower-speed running fatigue treadmill test, rats exposed to predator odor ran significantly (>5 min) longer than after control exposure (n=9). *Predator odor>control; ‡main effect of predator odor; §significant interaction.