Figure 2.
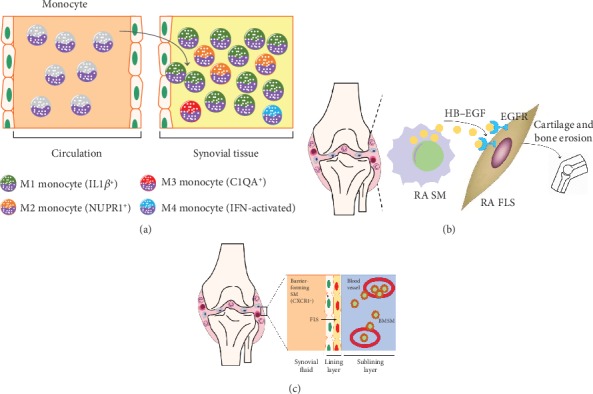
The heterogeneity of SMs in RA was discovered by single cell sequencing. (a) Accelerating Medicines Partnership Rheumatoid (AMPR) Arthritis consortium identified the unique activation states of synovial monocytes as four subsets: IL1β+ proinflammatory monocytes (M1), NUPR1+ monocytes (M2) with a mixture of leukocyte-poor RA cells, C1QA+ (M3), and IFN-activated monocytes (M4) by scRNA-seq analysis. (b) HBEGF+ inflammatory SMs are enriched in RA tissues and are shaped by FLS. These SMs promoted fibroblast invasiveness in an EGFR-dependent manner, indicating that intercellular cross talk in this inflamed setting reshapes both cell types and contributes to FLS-mediated cartilage and bone erosion. (c) Culemann et al. found that certain SMs form a cell layer that protects joints from the inflammatory immune-cell attacks on bone and cartilage. This barrier is formed in the lining layer (next to FLS). The barrier-forming SMs express proteins associated with a type of barrier-forming epithelial cell, and these proteins form structures called tight junctions. Barrier-forming SMs arise from a type of macrophage called an interstitial macrophage, which resides in the sublining layer. By contrast, nonresident macrophages enter the joint from blood vessels. These cells, which can drive inflammation, arise from monocytes.
