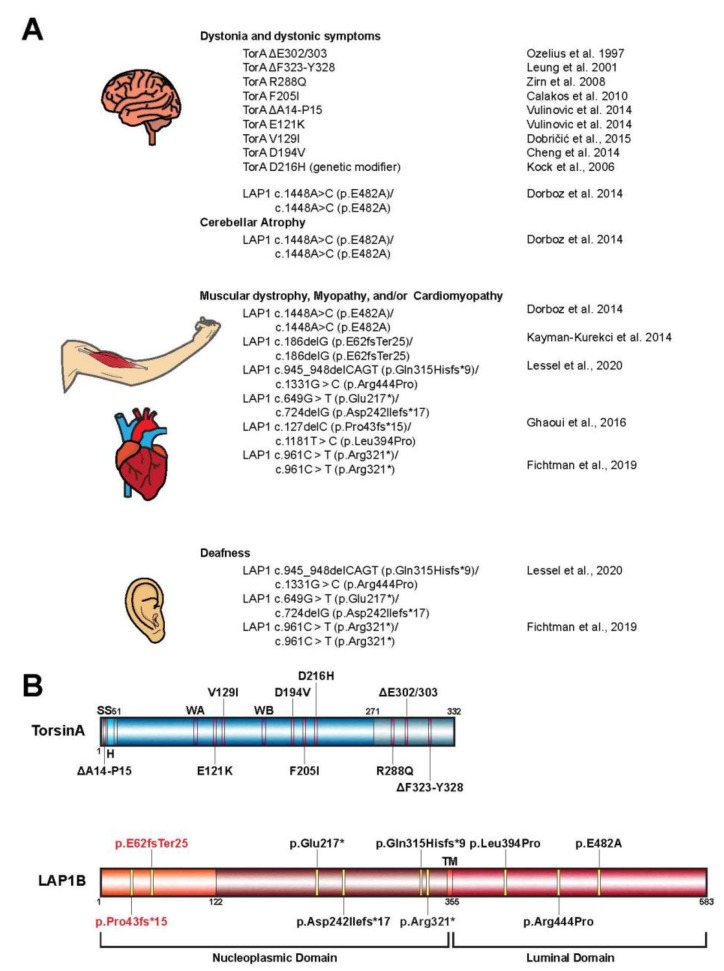
Figure 2.
(A) Mutations in TOR1A and TOR1AIP1 contribute to a variety of human disease pathologies. Shown is a comprehensive list of disease-associated mutations in the TOR1A (TorsinA) and TOR1AIP1 (lamina-associated polypeptide 1 or LAP1) genes. (B) Schematic representation of TorsinA and the LAP1 isoform LAP1B highlighting the alteration associated with the mutations from panel A. LAP1C is a shorter isoform of LAP1 that results from an alternative translation initiation site that ultimately leads to the absence of residues 1–121 [17]. All alterations, except for p.E62fsTer25 and p.Pro43fs*15 (red), are present in both isoforms. SS, signal sequence; H, hydrophobic region; WA, Walker A motif; WB, Walker B motif; TM, transmembrane helix.