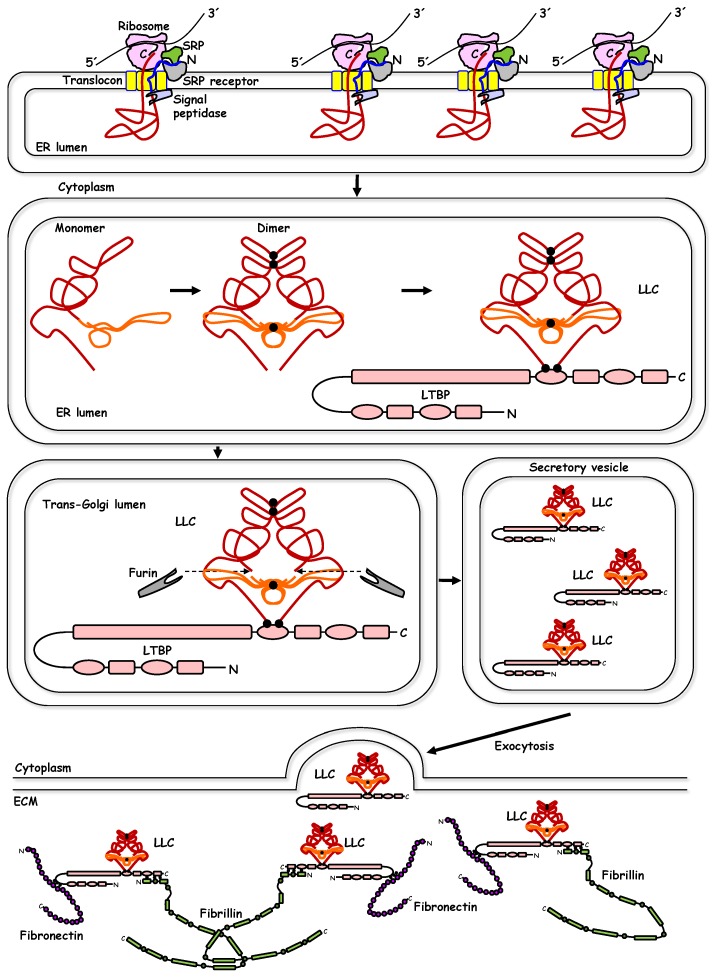
Figure 1.
Biosynthesis and extracellular deposition of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β). A sequence of biochemical events is shown from the top left to the bottom, guided by black arrows. Ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) translate the TGF-β mRNA (black line 5′-3’) into TGF-β protein (red line with blue signal peptide). The signal peptide associates with the signal recognition protein (SRP), which associates with the SRP receptor and the translated polypeptide is transported through the translocon channel into the lumen of the ER where the signal peptidase cleaves the signal peptide, generating a pro-TGF-β monomer that folds in the lumen of the ER (red polypeptide corresponds to the N-terminal long polypeptide known as latency associated peptide (LAP) and orange polypeptide correspond to the mature C-terminal polypeptide). The architecture of pro-TGF-β follows the crystallographic structure of the molecule. Dimerization of pro-TGF-β takes place in the ER lumen via three disulfide bonds (black dots), two in the prodomain and one in the mature domain. The dimeric pro-TGF-β crosslinks via disulfide bonds (black dots) to the latent TGF-β binding protein (LTBP) in the ER lumen, forming the large latent complex (LLC). The LLC translocates from the ER lumen to the cis- (not shown) and then to the trans-Golgi cisternae. For simplicity, the prodomain N-linked glycosylation is not shown. In the trans-Golgi, furin protease cleaves at the junction of the prodomain with the mature domain (dotted arrows). The cleaved LLC accumulates in secretory vesicles that undergo exocytosis and secrete the LLC to the extracellular environment where the LLC incorporates into the matrix (ECM). LLC crosslinking to fibrillin (three disulfide bonds, black dots) and to fibronectin (three more disulfide bonds, black dots) is shown. All relevant proteins are drawn emphasizing their domain architecture, without clarifying the identity of each domain.