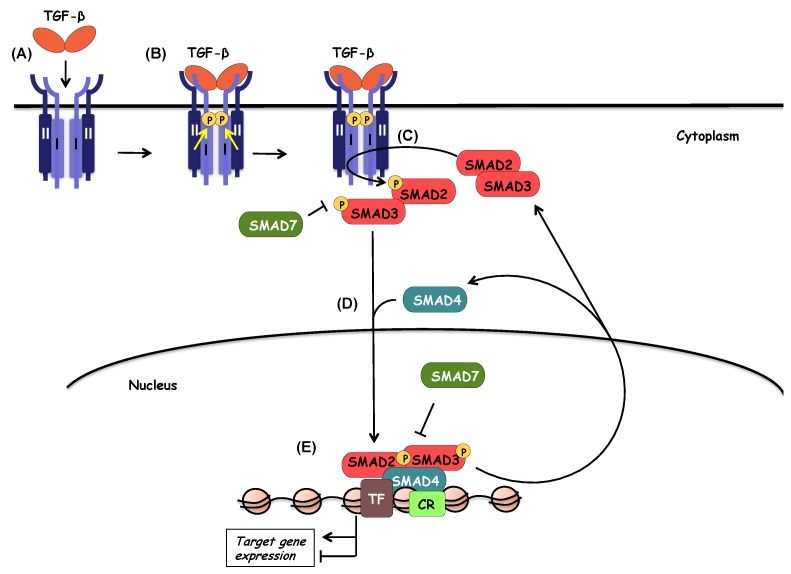
Figure 3.
The TGF-β/SMAD signaling pathway. During the first steps of TGF-β signaling, TGF-β ligand binds to a heteromeric complex of type II, and type I receptors (A). Upon ligand binding, type II receptor phosphorylates and activates type I receptor (B). Activated type I receptor in turn phosphorylates and activates the receptor-activated SMADs (R-SMADs), SMAD2 and SMAD3 (C). SMAD7 competes with R-SMADs for interacting with type I receptor, thus preventing R-SMAD activation and proper propagation of the signaling. Activated R-SMADs dissociate from type I receptors in order to form a complex with the common mediator SMAD4 (D). The trimeric complex translocates to the nucleus where it associates with high-affinity DNA binding transcription factors (TF) and chromatin remodeling proteins (CR) in order to positively or negatively regulate the transcription of target genes (E). SMAD7 can also inhibit the transcriptional activity of the nuclear SMAD complex.