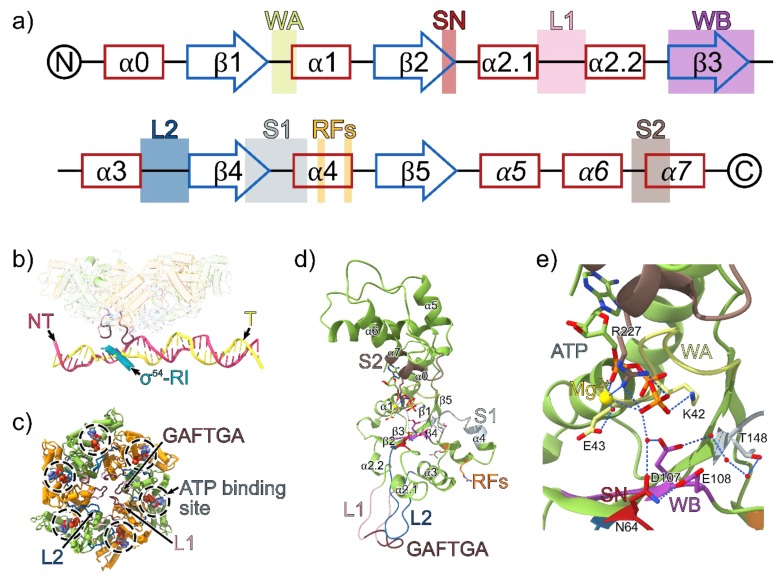
Figure 3.
(a) The secondary structure of clade 6 AAA+ proteins with the positions of the conserved AAA+ motifs indicated. α helices are shown in red and β sheets are shown in blue. The α-helices in the lid subdomain are italicised. WA = Walker A, SN = Switch asparagine, L1 = Loop 1, WB = Walker B, L2 = Loop 2, S1 = sensor 1, RF = R fingers, S2 = Sensor 2. (b) The phage shock protein F (PspF) hexamer, σ54 region I (RI) and promoter DNA from the RPi structure (PDB ID: 5NSS). The highly conserved GAFTGA motif on the L1 loop projects downward from the plane of the PspF ring and contacts σ54-RI and the −11/−12 region on the promoter DNA. PspF monomers in the ring are coloured in green and orange; template strand (T), yellow; non-template strand (NT), pink; σ54-RI, cyan. (c) The PspF AAA+ domain hexamer from the viewpoint of the promoter DNA. ATP molecules are superimposed on the structure based on the ATP bound PspF crystal structure (PDB ID: 2C96). (d) PspF monomer model based on the crystal structure of an individual monomer of the AAA+ domain of PspF bound to ATP (PDB ID: 2C96). The solvent and magnesium atoms are superimposed from the ATP-bound PspFR227A AAA+ domain (PDB ID: 2C9C), and the missing parts of the L1 and L2 loops are modelled from the ATP bound structure of NtrC1E239A AAA+ domain (PDB ID: 3M0E). (e) The ATP binding site interactions within a PspF monomer.