Figure 6.
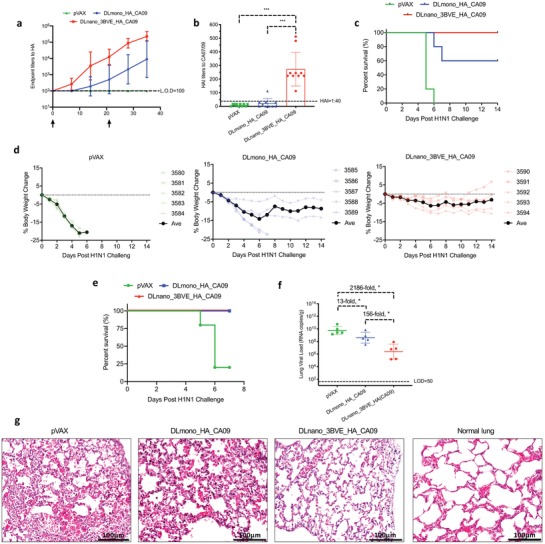
Functional evaluations of DLmono_HA_CA09 versus DLnano_3BVE_HA_CA09 in H1 A/California/07/09 lethal challenge model. a) Binding endpoint titers to HA (CA09) over time in BALB/c mice immunized with two 1 µg doses of pVAX, DLmono_HA_CA09, or DLnano_3BVE_HA_CA09 3 weeks apart. b) HAI titers to the autologous A/California/07/09 strain in BALB/c mice immunized with 1 µg pVAX, DLmono_HA_CA09, or DLnano_3BVE_HA_CA09 5 weeks from their first vaccination. c) Percentages of vaccinated mice surviving the lethal 10LD50 H1/A/California/07/09 challenge over 2 week period. d) Weight changes in mice immunized with pVAX, DLmono_HA_CA09, or DLnano_3BVE_HA_CA09 over 2 week period following 10LD50 H1/A/California/07/09 challenge. e) Percentages of vaccinated mice surviving the lethal 10LD50 H1/A/California/07/09 challenge over 7 day period in a separate study. f) Lung viral load in challenged mice at 7 days post‐challenge or at the time of euthanasia as determined by RT‐qPCR. g) H&E stain for lung histopathology in mice 7 days after viral challenge or at the time of euthanasia, normal lung histology is shown for comparison; scale bar represents 100 µm. Each group contained 10 mice in panels (a and b); each group contained five in the remaining panels; each dot represents a mouse; error bar represents standard deviation; arrow below the plot represents an immunization; two‐tailed Mann–Whitney rank test used to compare groups; p‐values were adjusted for multiple comparison where appropriate; *p < 0.05.
