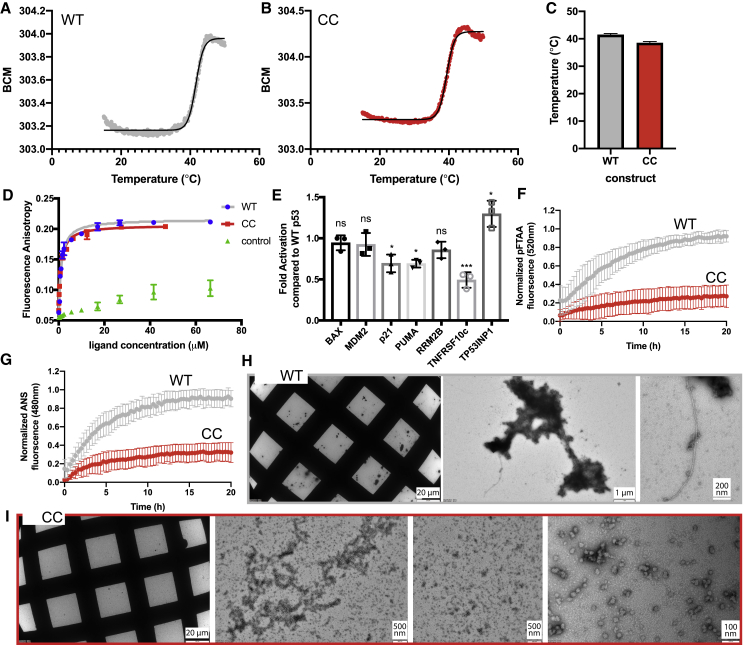
Figure 5.
Biophysical Analysis of p53cc
(A) Heat denaturation of WT p53DBD, monitored by intrinsic fluorescence plotted as the barycentric mean (BCM) of the emission spectrum. The black line indicates the fit performed to determine the midpoint of the transition.
(B) Same as (A) but for the CC mutant.
(C) Average Tm values obtained from five biological replicate measurements.
(D) DNA-binding affinity of p53cc and the WT, measured by FA. Error bars indicate standard deviation of five biological replicates, each measured in three technical replicates.
(E) Degree of promoter activation of p53cc relative to WT p53 in Saos-2 cells, measured by qPCR. Error bars indicate standard deviation of three biological replicates, each measured in three technical replicates.
(F) Aggregation kinetics of p53cc and the WT, measured by p-FTAA fluorescence.
(G) Aggregation kinetics of p53cc and the WT, measured by ANS fluorescence.
(F and G) Error bars indicate standard deviation of five biological replicates, each measured in three technical replicates.
(H) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis of aggregates of WT p53.
(I) TEM analysis of p53cc.
(H and I) Representative images from three biological replicates.