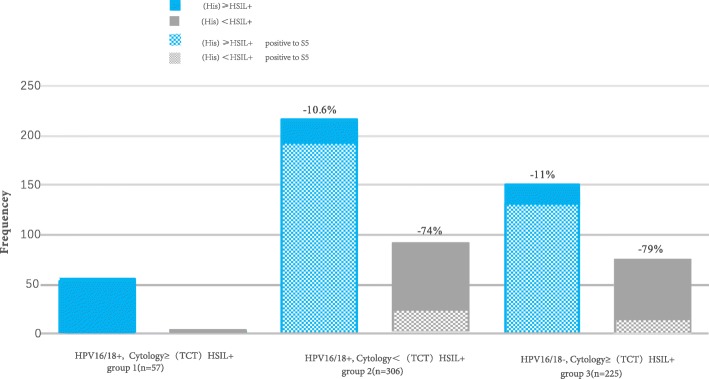
Fig. 5.
Advantage of conducting S5 classifier as a second triage tool for colposcopy referral for HSIL+ endpoint. We defined three risk groups of women based on the results of HPV16/18 detection and cytology. The group 1 consisted of HPV16/18+ and cytology ≥ (TCT)HSIL+ women. Of all the 57 women in group 1, fifty-six (98.2%) cases were histopathological HSIL+ women; we consider that these women should be referred to colposcopy based on the first triage alone. Group 2 represented a triage discrepancy consisting of HPV16/18+ but cytology < (TCT)HSIL+ women. The use of S5 methylation as a second triage test in this group would have reduced colposcopy referral by 74% for a HSIL+ endpoint (p = 0.000). In group 3, women were HPV16/18− but cytology ≥ (TCT)HSIL+, and the use of S5 methylation would have reduced colposcopy referral by 79% for a HSIL+ endpoint (p = 0.000). In the both group 2 and group 3, the sensitivity of S5 as the second triage test decreased slightly than in a scenario where all women were referred to colposcopy, but reduce the numerous unnecessary colposcopy referrals by more than 70% to detect HSIL+. The frequency shows the number of women in each group. No lesion, histologically negative without squamous intraepithelial lesion; LSIL, low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; HSIL, high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; CC, cervical cancer; (TCT)HSIL+, cytological high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion or worse