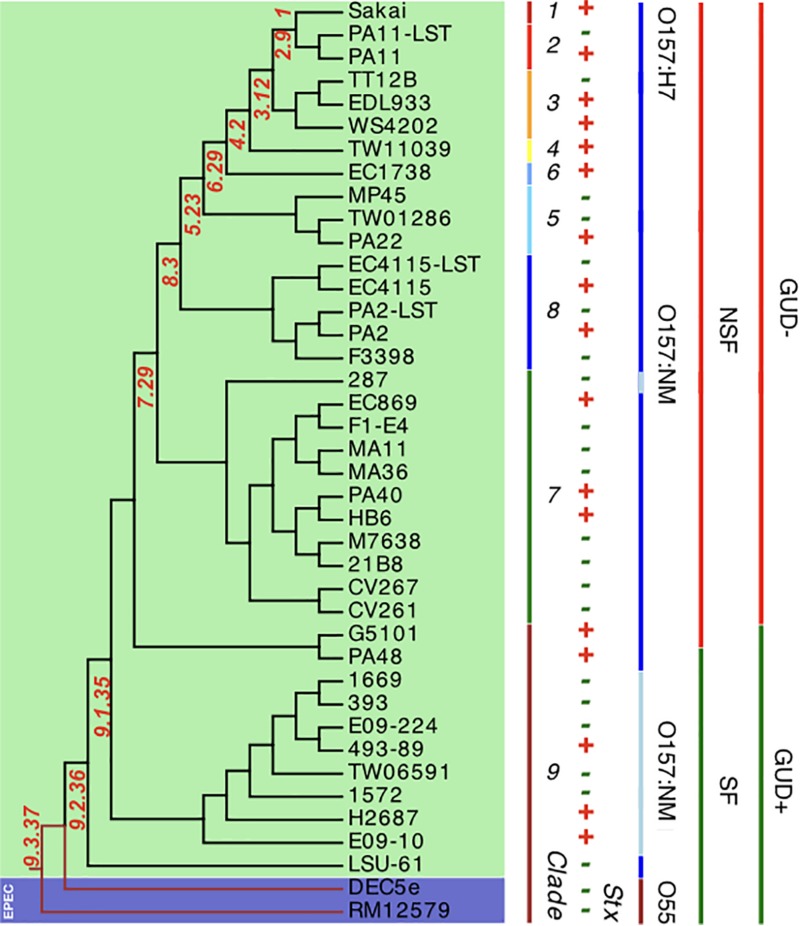
FIGURE 3.
Core genome SNP phylogeny of Stx (±) O157:H7 and SF O157:NM. Comparison of 40 (LST–) EHEC O157:H7 and SF O157:NM genomes and two ancestral EPEC O55:H7 yielded a total of 7,673 SNPs (Supplementary Table S1), of which 4,109 were parsimony informative. The tree shown is the majority-consensus tree of 281 equally parsimonious trees with a CI of 0.98. Trees were recovered using a heuristic search in PAUP (Wilgenbusch and Swofford, 2003) with 100 bootstrap replicates. The tree was visualized in Geneious (Kearse et al., 2012) and decorated with strain-associated metadata in EvolView (Zhang et al., 2012; He et al., 2016), such as clade assignment, Stx-, SF-, and GUD-status. As evident from comparing the topology to the WGA tree (Supplementary Figure S2), major clusters are mirrored. The tree topology partitions the isolates into distinct phylogenetic clusters that are in accordance with the stepwise model of EHEC O157:H7/NM evolution from an EPEC O55:H7 progenitor.