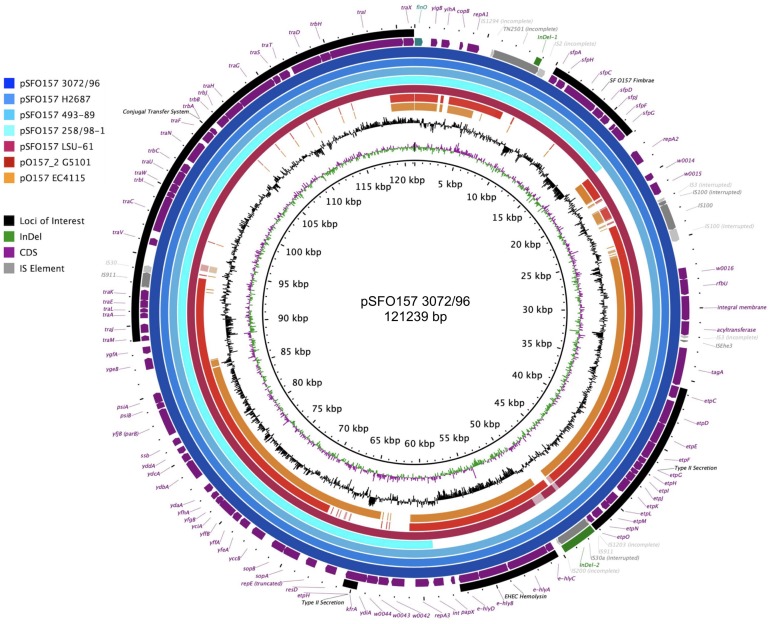
FIGURE 4.
Comparison of the three major virulence plasmid variants. BRIG analysis of plasmid architecture and gene inventory of the three established virulence plasmid variants inferred from representative closed plasmids. Respective gene inventories are referenced to the largest 121-kb pSFO157 variant of strain 3072/96 (Brunder et al., 2006) shown on the outermost circle. CDS of reference plasmid are presented as purple arrows and functional annotation for loci of importance are depicted in the legend. The finO gene defines the origin of replication and is the designated pSFO157+1 start site. Query plasmids are plotted on each circle as shown in the legend and the order reflects phylogenomic position according to the stepwise model of O157:H7 evolution. Different color codes of the circles represent distinct plasmid types: Plasmid pSFO157 present in SF O157 strains (blue) H2687, 493-89, 258/98-1 (a 79-kb truncated variant), and O157:H7 strain LSU-61 (burgundy); and the O157:H7 plasmid types pO157 and pO157_2 from EC4115 (orange, 94,644 kb) and G5101 (red, 89,762 kb), respectively. Major differences are associated with MGEs highlighted in gray. The gene inventory of pSFO157 is distinguished from pO157 and pO157_2 by the presence of the Sfp fimbriae and an incomplete F-plasmid like conjugal transfer machinery, which accounts for the one-third larger pSFO157 plasmid size. The hly and etp operons in pSFO157-258/98-1 from the Czech Republic was lost as part of a 41,534 bp fragment via homologous recombination. GC-skew and -content of the pSFO157 3072/96 reference plasmid are depicted in the two innermost circles, respectively.