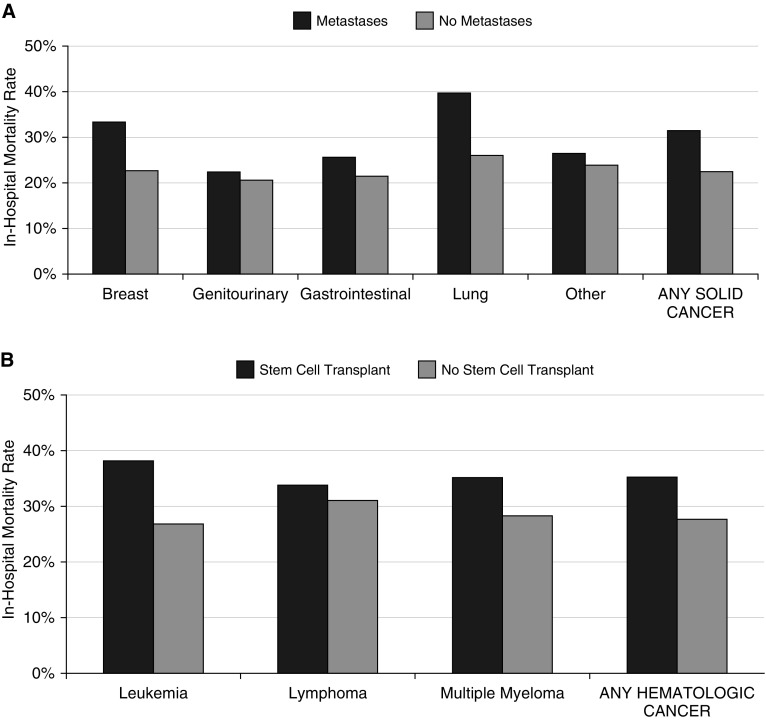
Figure 2.
Sepsis-associated in-hospital mortality rates by specific solid and hematologic cancer diagnosis categories. (A) Sepsis-associated mortality rates for patients with solid cancer, stratified by the presence of metastases. Sample size: breast (n = 213 with mets vs. 150 with no mets), genitourinary (n = 298 vs. 298), gastrointestinal (n = 822 vs. 529), lung (n = 848 vs. 143), other (n = 591 vs. 902), and overall (n = 2,979 vs. 1,644). (B) Sepsis-associated mortality rates for patients with hematologic cancer, stratified by presence of stem cell transplant. Sample size: leukemia (230 with stem cell transplant vs. 383 with no transplant), lymphoma (171 vs. 915), multiple myeloma (51 vs. 251), and overall (413 vs. 2,453). mets = metastases.