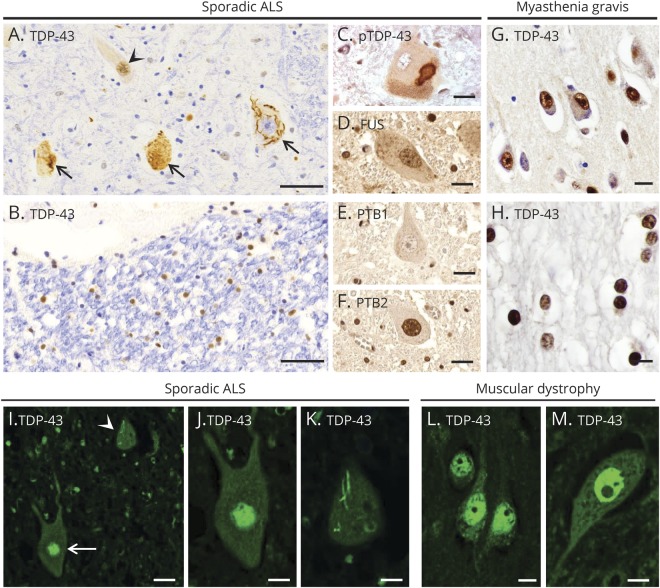
Figure 1. Expression pattern of RNA-binding proteins in ALS and a control patient and two patients with normal CNS.
(A–F) A case of sporadic ALS. (A) TDP-43 is expressed normally in the nucleus of some spinal cord motor neurons (arrowhead), but depleted from the nucleus of affected motor neurons, forming aggregates (large arrows). (B) TDP-43 is in its normal nuclear location in glial cells in spinal cord white matter. (C) A cytoplasmic inclusion in spinal cord motor neurons contains pTDP-43. As expected in normal motor neurons, (D) FUS is present in the nucleus, (E) PTB1 is not present, and (F) PTB2 is present in the nucleus. (G and H) A CNS control patient with myasthenia gravis. Expression of TDP-43 is mainly seen in the nuclei of cortical neurons (G) and white matter oligodendrocytes (H). (I–K) An additional case of sporadic ALS. (I) Immunofluorescent staining for TDP-43 shows normal expression in the nucleus of 1 spinal cord motor neuron (arrow), but mislocalization to the cytoplasm (arrowhead) in another neuron. (J and K) High magnification view of the 2 motor neurons shown in panel I, with normal nuclear expression of TDP-43 in 1 neuron (J), but nuclear depletion of TDP-43 along with a skein-like cytoplasmic inclusion in another neuron (K). (L and M) A CNS control patient with muscular dystrophy. TDP-43 expression is seen in the nucleus of cortical neurons (L) and spinal cord motor neurons (M). Scale bars: 50 μm (A and B), 20 μm (C–G, I), and 10 μm (H, J–M). ALS = amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; FUS = fused in sarcoma; PTB = polypyrimidine tract–binding protein; pTDP-43 = phosphorylated TDP-43; TDP-43 = transactivation response DNA-binding protein of 43 kDa.