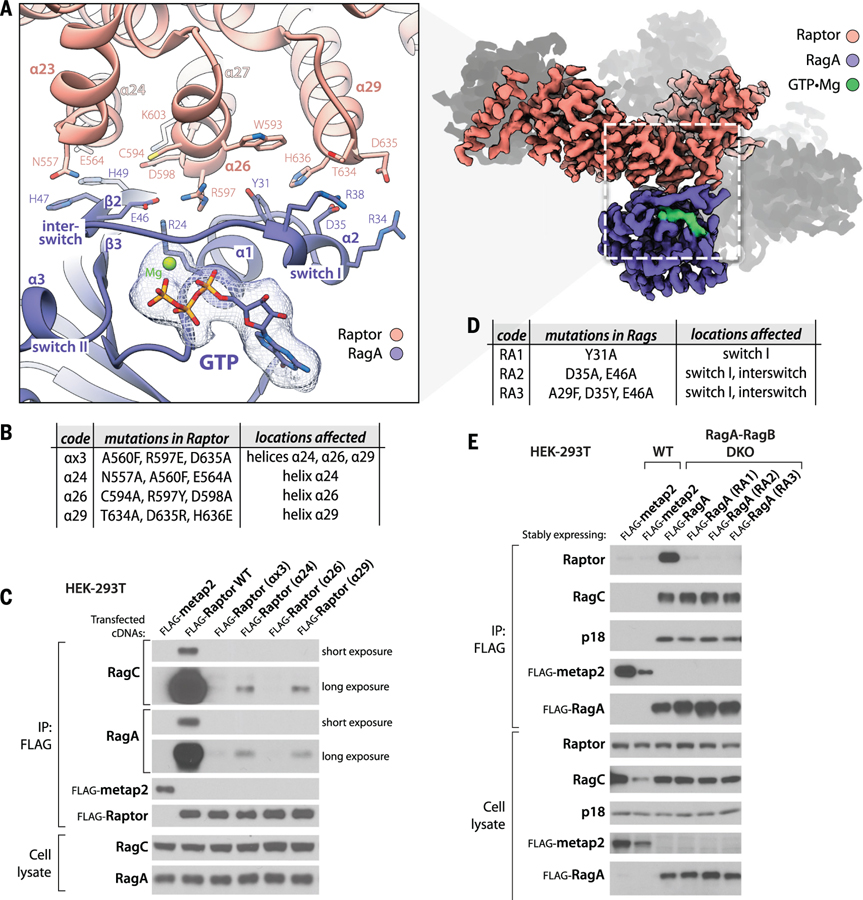
Figure 2. Raptor-RagA interaction.
(A) Three helices (α24, α26, α29) in the HEAT-repeat domain of Raptor directly engage the switch-I face of GTP-loaded RagA. (B) Description of mutations introduced in the RagA-binding helices of Raptor. (C) Mutations in these helices render Raptor expressed via cDNA transient transfection unable to co-immunoprecipitate the endogenous RagA-RagC heterodimer. (D) Description of mutations introduced in the Raptor-binding region of RagA. (E) In RagA-RagB DKO HEK-293T cells, the transiently expressed RagA mutants in (D) cannot bind endogenous Raptor but have an intact capacity to bind to RagC and Ragulator, as assessed by its p18 subunit. Flag-metap2 was used as a control protein.