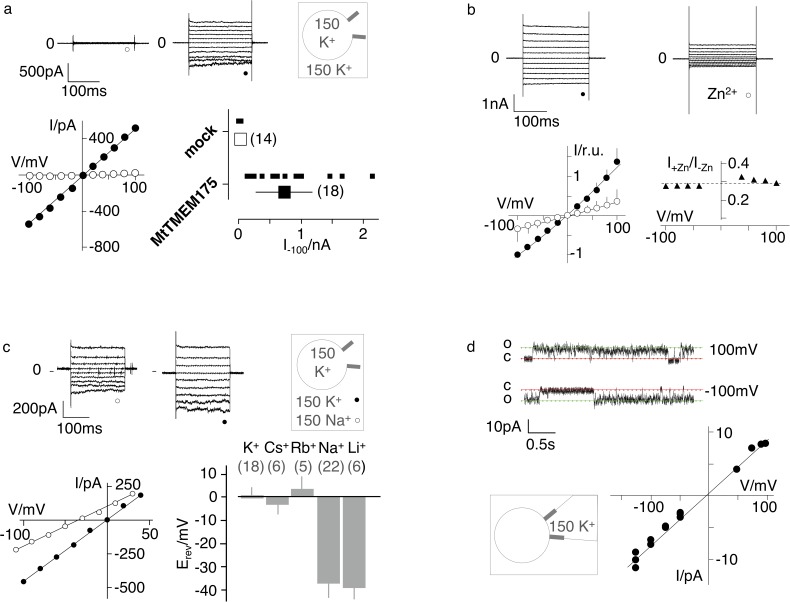
Figure 2. Electrophysiological characterization of MtTMEM175.
(a) Current responses to standard voltage pulse protocol in mock (○) and MtTMEM175 (⚫) transfected HEK293 cells (upper panel) and corresponding steady state I/V relations (lower left). Plot of currents recorded in same manner at −100 mV for individual cells (small symbols) and mean ±s.d. (large symbols) (lower right). Number of cells in brackets. (b) HEK293 cells expressing MtTMEM175 before (⚫) and after (○) adding 5 mM ZnSO4 to the bath solution containing 150 mM K+ (upper panel). Mean I/V relation (bottom left) of n = 4 cells (±s.d.). To compare the effect on different cells the I/V relation was normalized to currents at −100 mV in the absence of blocker (bottom left). The voltage dependency of the Zn2+ block was estimated by dividing currents in the presence and absence of Zn2+ (I+Zn/I-Zn) (bottom right) (c) HEK293 cells expressing MtTMEM175 (top row) before (left) and after (middle) replacing Na+ (○) with K+ (⚫) in the external buffer and corresponding I/V relation (bottom left). Same experiments were performed by exchanging K+ in external buffer by other cations. The mean reversal voltage (Erev) (±s.d., number of cells in brackets) is depicted in lower right panel. (d) Exemplary channel fluctuations at ±100 mV measured in cell-attached configuration on HEK293 cells expressing MtTMEM175 (upper) and pooled unitary I/V relation of single channel events from 10 measurements in four different cells (lower right) using standard bath and pipette solutions.