Figure 3.
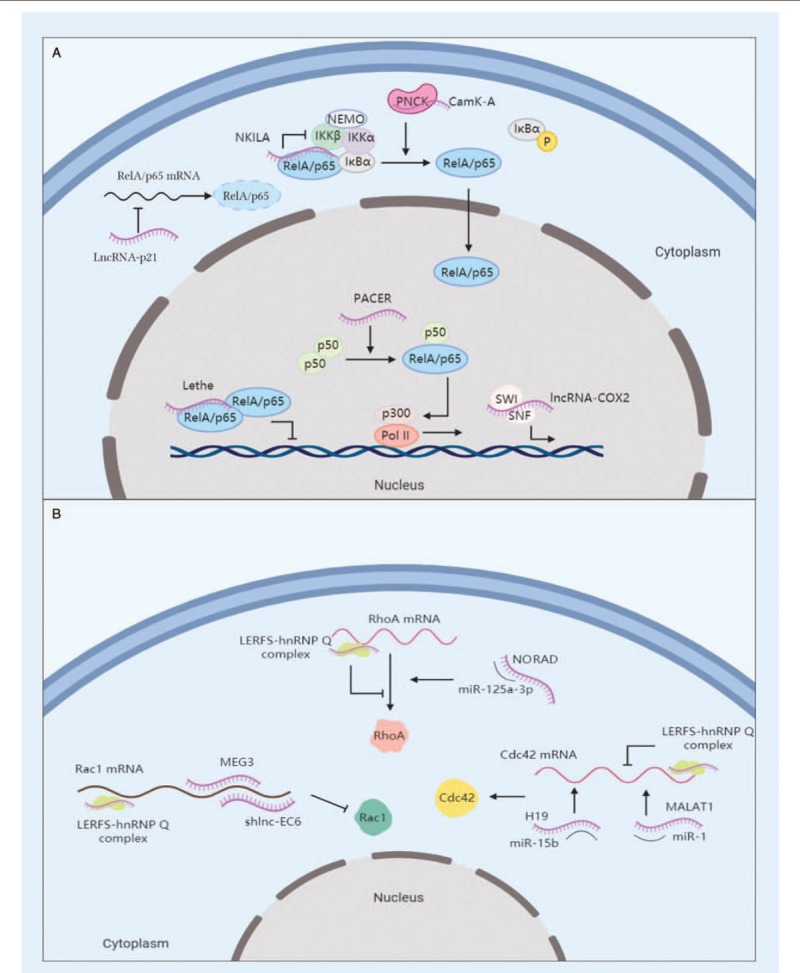
Functional lncRNAs in signaling pathway. (A) LncRNAs regulate NF-κB signaling pathways. NKILA masks the phosphorylating sites of IKKβ in IκBα-RelA complex and suppresses RelA activation. LncRNA-p21 sequesters RelA by suppressing its mRNA translation. Lethe blocks the DNA-binding activity of RelA homodimer. PACER sequesters p50 and facilitates the formation of Pol II transcriptional complex. LncRNA-Cox2 is integrated into the SWI/SNF complex and transactivates late-primary response genes regulated by NF-κB. CAMK-A, in accompany with calmodulin-dependent kinase PNCK, promotes IκBα phosphorylation and nuclear transportation of RelA. (B) LncRNAs participate in the regulation of RhoGTPases-mediating pathways. Newly-identified lncRNA LERFS forms a complex with hnRNP Q to interfere the translation of RhoA, Rac1, and Cdc42. NORAD, MEG3, shlnc-EC6, H19, and MALAT1 act as miRNA sponges to regulate the translation of the aforementioned RhoGTPases, respectively. IKK: Inhibitory-κB kinase; lncRNA: Long non-coding RNA; NEMO: NF-κB essential modulator; NF: Nuclear factor; NKILA: NF-κB interacting lncRNA; PNCK: Pregnancy upregulated non-ubiquitous calmodulin kinase.
