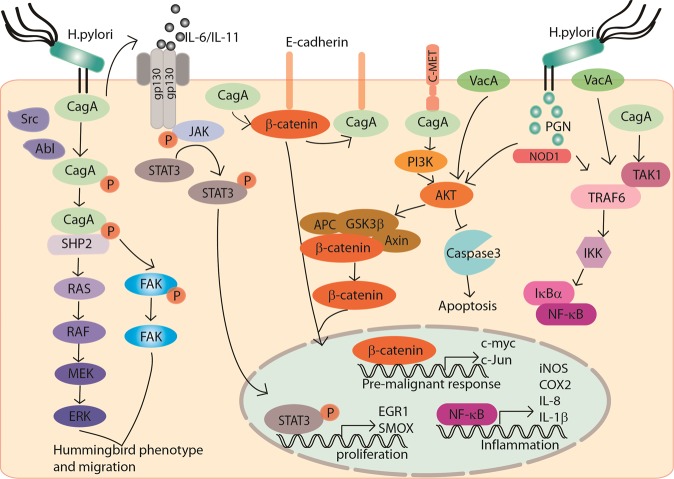
Fig. 1. Molecular pathogenesis of H. pylori in gastric carcinogenesis.
The MEK–ERK and FAK signaling pathways are activated by phosphorylated CagA to mediate hummingbird phenotype of the epithelial cells and promote cell migration. The β-catenin is activated by nonphosphorylated intracellular CagA by disruption of the E-cadherin–β-catenin complexes or PI3K–AKT signaling. CagA activates JAK-STAT3 pathway by releasing IL-6/IL11 and activating gp130. Nuclear translocation of STAT3 initiates gene expression for cell proliferation. H. pylori peptidoglycan and VacA potentiate PI3K–AKT signaling to promote epithelial cell migration, increase proliferation, and reduce apoptosis. CagA, VacA, and peptidoglycan coordinate to activate NF-κB signaling cascade thus to transcriptionally upregulate proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1 and IL-8, and promote inflammation.