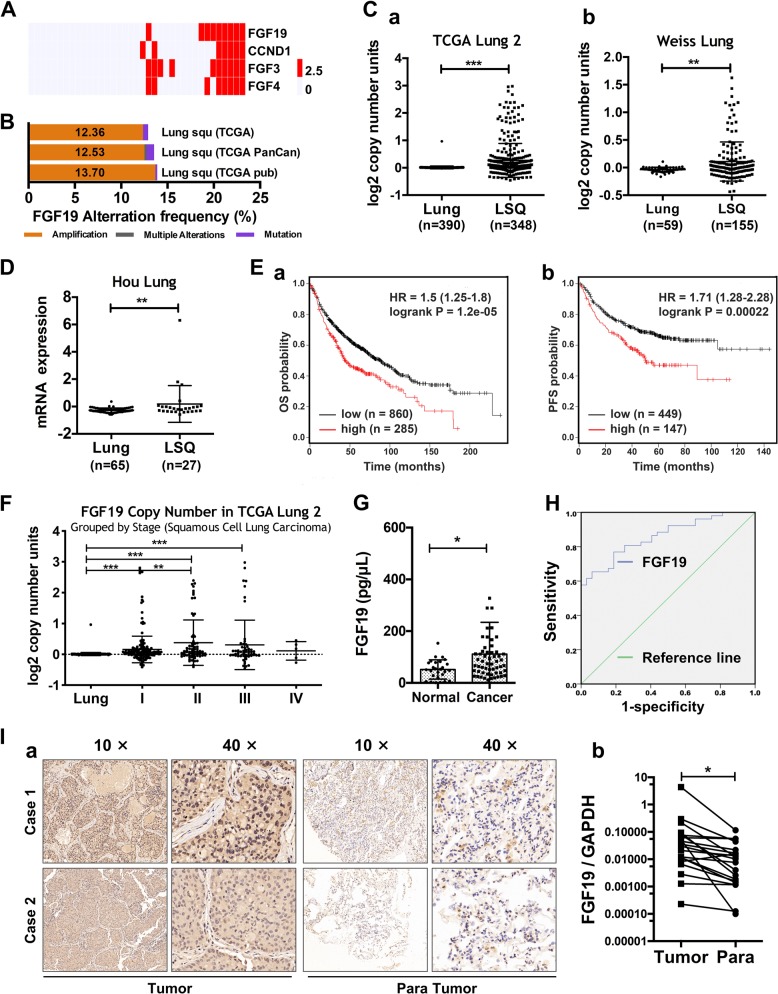
Fig. 1. FGF19 is amplified and overexpressed in patients with LSQ.
a Copy number variation (CNV) distribution of FGF19 in our LSQ cohort (n = 37). Mutations including 5 missense mutations (2 duplicate mutation): R151L, P191L, P199A; 1 truncating nonsense mutation: G205* and 1 fusion: ANO1-FGF19. b RNAseq expression analysis of FGF19 showing significantly high amplification in TCGA LSQ cases. c Copy number analyses of FGF19 in the Oncomine database with provisional LSQ cohorts in TCGA Lung2 datasets (a) and Weiss Lung datasets (b). d Expression of FGF19 in the Oncomine database with provisional LSQ cohorts in Hou Lung datasets. e Kaplan–Meier survival analysis based on RNAseq expression of FGF19 (higher FGF19 level: top 25%, lower FGF19 level: bottom 25%) on the overall survival (OS; n = 1145) (a) and progression-free survival (PFS; n = 596) (b) in lung cancer patients (http://www.kmplot.com). f Copy number of FGF19 grouped by stage of samples in TCGA Lung2 datasets from the Oncomine database with provisional LSQ cohorts. g Serum levels of FGF19 in NSCLC patients (n = 57) were significantly higher than in control subjects (n = 27). h Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis of serum FGF19 levels in 57 NSCLC patients vs. 27 controls (*p < 0.05). i Representative IHC results for FGF19 expression in LSQ tissue arrays (a) and quantitative data of staining intensity presented as positive area score (b). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.