Fig. 2. Schematics showing SETDB1-mediated long-range chromatin loop interactions.
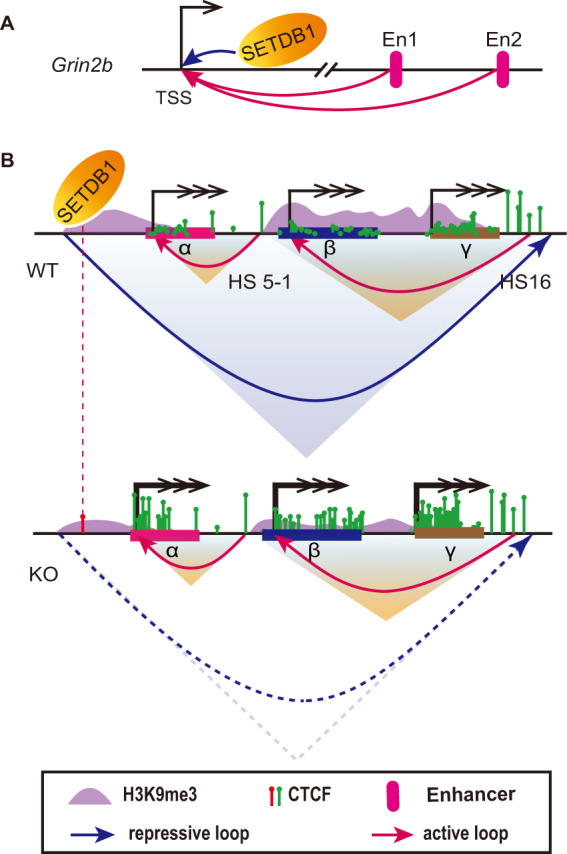
a Grin2b gene locus and the transcriptional starting site (TSS), and enhancers (En), En1 and En2. b Pcdh gene clusters in neurons from Setdb1 wildtype (WT) mice (top) and knockout (KO) mice (bottom). SETDB1-mediated long repressive loop (solid blue line with arrow) is essential for large TAD conformation (∇ in blue) in WT; but not Setdb1 KO neurons (indicated by dashed lines). Compared with WT, the level of H3K9me3 (shaded in purple) is lower in KO neurons, while the CTCF signal (matchsticks in green and red, with red indicating the potential SETDB1 binding site) and α-, β-, γ-Pcdh gene transcription (multi-tailed arrows indicate multiple genes in these clusters) are significantly higher in KOs. There is no difference between enhancers for HS 5-1 and HS 16-20 mediated active loops (solid red line with arrow) and nesting TADs (∇ in red) between WT and KO neurons.
