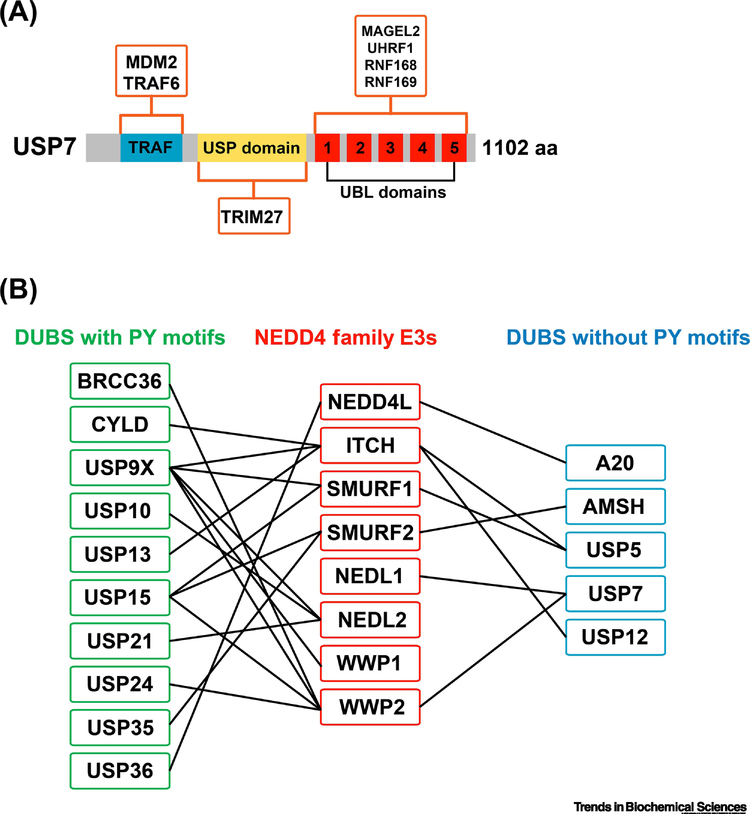
Figure 2.
E3-DUB hubs in the ubiquitin network. (A) USP7 is the DUB with the most reported E3 interactions. A schematic representation of the USP7 domain structure is depicted, illustrating the location of the TRAF domain (blue), the USP catalytic domain (yellow), and the five C-terminal ubiquitin-like (UBL) domains (red). Orange boxes illustrate interactions where the specific domain of USP7 that binds to the specified E3 has been mapped. (B) Many DUBs are reported to interact with NEDD4 family E3 ubiquitin ligases (boxed in red, middle). Many of the NEDD4-interacting DUBs harbor PY motifs (boxed in green, left), while a few lack PY motifs (boxed in blue, right). The preponderance of NEDD4 family interactions with PY motif-containing DUBs suggests that many occur via WW domain scaffolding, although in most cases experimental evidence on the biochemical basis of interaction is lacking.