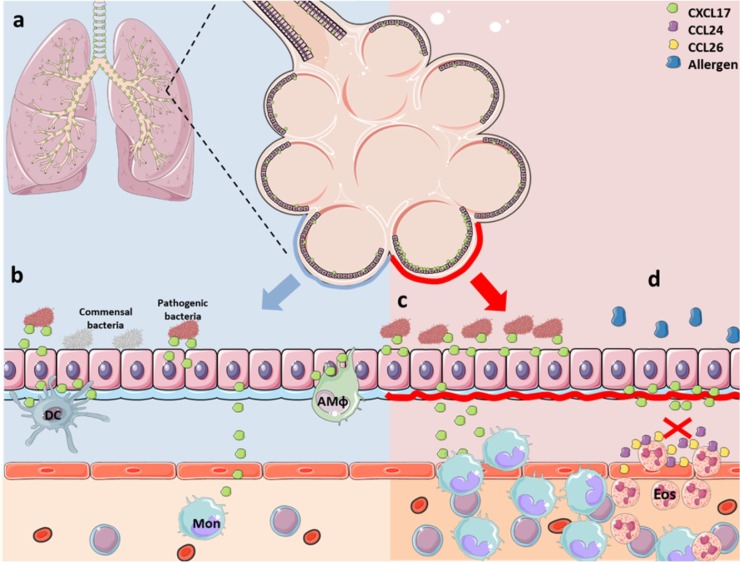
Fig. 1.
Biological activities of CXCL17.
The functions of CXCL17 are illustrated by exemplifying its possible participation in the maintenance of homeostasis of the respiratory tract. (a) CXCL17 expression is restricted to the lining epithelium of the airways and distant alveoli. (b) CXCL17 has a potent bactericidal activity over pathogenic bacterial strains, but not against commensal bacteria, suggesting a role in shaping the composition of bacterial community residing at different epithelial surfaces. In addition, CXCL17 controls the recruitment of certain subsets of myeloid cells, such as dendritic cells, monocytes and macrophages across the endothelium into the epithelium. (c) During mucosal infections, production of CXCL17 may increase to counteract bacterial replication by its direct antimicrobial activity, or via regulating the infiltration of myeloid cells into the infected epithelium. (d) CXCL17 also plays an anti-inflammatory role, as illustrated in the case of eosinophilic inflammation of the airways elicited by allergens in patients with type 2 asthma. In these settings, CXCL17 inhibits the production of chemokines important for the recruitment of eosinophils, such as CCL24 and CCL26. AMφ, alveolar macrophages; DC, dendritic cells; Eos, eosinophils; Mon, monocytes. The art pieces used in this figure were modified from Servier Medical Art by Servier, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://smart.servier.com/).