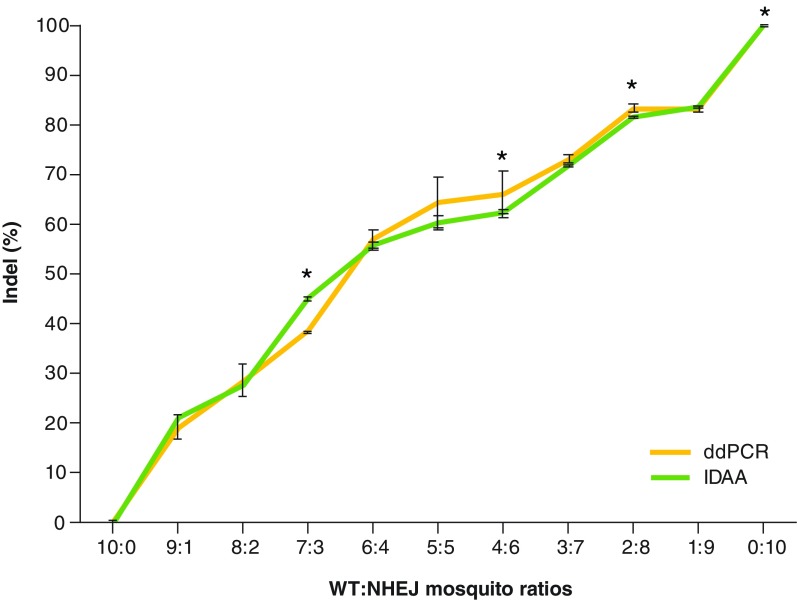
Figure 2. . Quantification of nonhomologous end joining alleles in AsMCRkh2 mosquito samples by ddPCR and IDAA techniques.
DNA was extracted from 15 to 10 mosquito pools. To assess the sensitivity of both techniques, the mosquito pools consisted of a mix of WT and NHEJ mosquitoes at 11 different ratios of WT:NHEJ (10:0, 9:1, 8:2, 7:3, 6:4, 5:5, 4:6, 3:7, 2:8, 1:9 and 0:10). DNA was used for PCR, and amplicons were subjected to IDAA and ddPCR analysis to determine the indel percentage in each sample. Each ratio was conducted in triplicate (n = 3), and average results were compared between the two techniques. Although deviating from theoretical indel percentages (40% indel for a 6:4 ratio), both techniques demonstrated precision based on producing similar results for each ratio and having a Pearson correlation coefficient of r = 0.99. In addition, values provided by ddPCR and IDAA are also representative of their accuracy; because both deduced the same indel percentage, it is likely close to the actual indel percentage. Student's t test was performed to compare the measurements at each ratio (*p < 0.05).
ddPCR: Droplet Digital PCR; IDAA: Indel detection by amplicon analysis; Indel: Insertions or deletion; NHEJ: Nonhomologous end joining; WT: Wild-type.