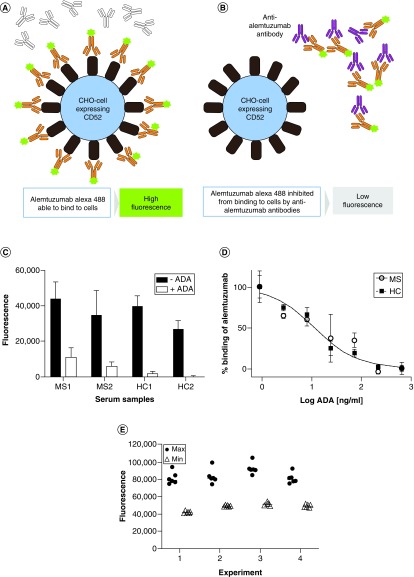
Figure 2. . Schematic of the assay format.
(A) In the absence of ADA, Alemtuzumab–Alexa Fluor 488 binds to the cells resulting in a high fluorescence signal. (B) In the presence of neutralizing ADA, the Alemtuzumab–Alexa Fluor 488 is prevented from binding to the cells, resulting in a loss of fluorescence. (C) Serum samples from an MS patient and healthy individuals not treated with alemtuzumab were spiked with anti-alemtuzumab and assayed for inhibiting alemtuzumab–Alexa Fluor 488 binding to CHO-CD52 cells using fluorescence measurement on a Clariostar Plus plate reader and the data plotted using GraphPad Prism. (D) Serum samples from an MS patient and a healthy individual not treated with alemtuzumab were spiked with anti-alemtuzumab, threefold serially diluted and assayed for inhibiting alemtuzumab–Alexa Fluor 488 binding to CHO-CD52 cells using fluorescence measurement on a Clariostar Plus plate reader and the data plotted using GraphPad Prism. (E) The maximum and minimum fluorescence (n = 6) were determined in four experiments, and the data plotted using GraphPad Prism.
ADA: Antidrug antibody; CHO: Chinese hamster ovary; MS: Multiple sclerosis.