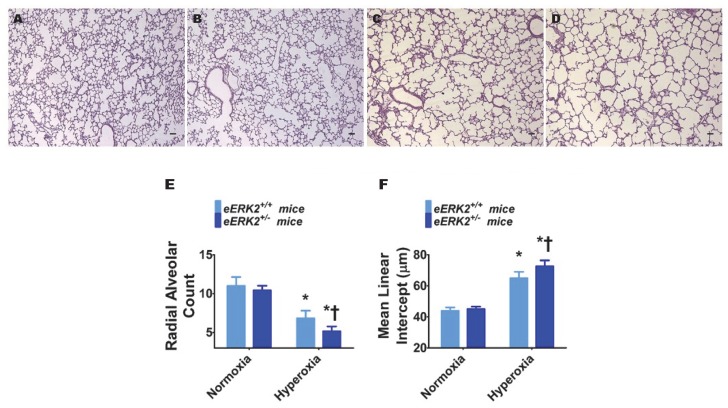
Figure 3.
Lung alveolarization in endothelial ERK2-sufficient (eERK2+/+) or -deficient (eERK2+/−) mice exposed to hyperoxia. One-day-old eERK2+/+ or eERK2+/− mice were exposed to either 21% O2 (normoxia) or 70% O2 (hyperoxia) for two weeks, after which the lungs were harvested for lung morphometry. (A–D) Representative hematoxylin and eosin-stained lung sections from eERK2+/+ (A,C) and eERK2+/− (B,D) mice exposed to normoxia (A,B) or hyperoxia (C,D). Scale bar = 100 µm. (E,F) Alveolarization was quantified by determining radial alveolar counts (RAC) (E) and mean linear intercepts (MLI) (F). Values are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 4–5/genotype/exposure). Significant differences between eERK2+/+ and eERK2+/− mice in hyperoxic conditions are indicated by †, p < 0.05. Significant differences between normoxia and hyperoxia groups are indicated by *, p < 0.05 (ANOVA).