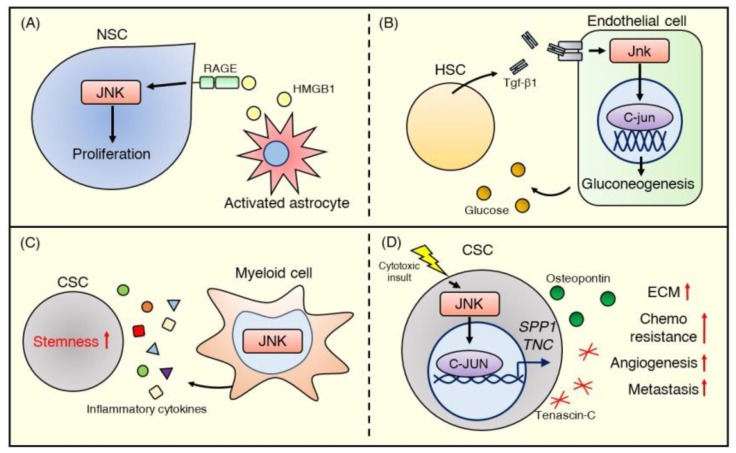
Figure 5.
JNK signaling in the stem cell niche. (A) HMGB1 released from activated astrocytes stimulates the RAGE-JNK pathway and promotes the proliferation of NSCs. (B) Embryonic HSCs stimulate endothelial cells with Tgf-β1 to encourage glucose production and HSC emergence via activating the Jnk–C-jun signaling pathway. (C) JNK signaling contributes to myeloid cell function in the CSC niche. JNK-deficient myeloid cells in the liver exhibit reduced secretion of inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α), which promote CSC stemness. (D) JNK signaling in breast cancer mediates ECM production. The JNK–C-JUN pathway, stimulated by cytotoxic stress, upregulates gene expression in the ECM, wound healing, and stem cells and promotes the production of matricellular proteins such as osteopontin and tenascin C, encoded by SPP1 and TNC, respectively. These proteins activate angiogenesis and further ECM production in the CSC niche and subsequently promote metastasis and chemoresistance.