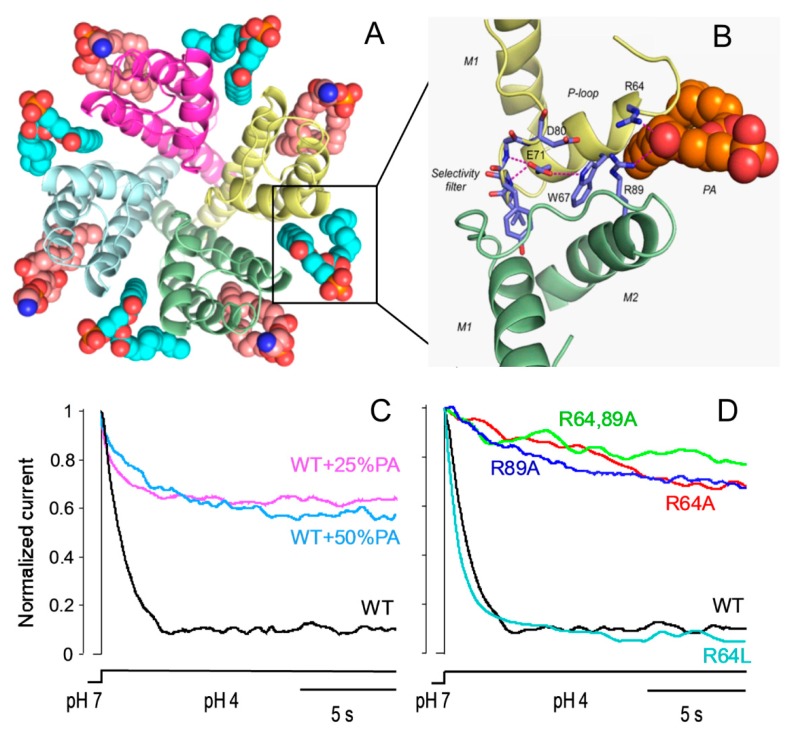
Figure 2.
Lipid modulation of KcsA inactivation by binding of non-annular anionic lipids. In (A), a top view molecular model of KcsA with annular (acyl chains in light pink) and non-annular (acyl chains in cyan) lipids is shown. In (B), a zoom of a non-annular lipid binding site is depicted, with a PA molecule bound. In (C,D), normalized KcsA macroscopic currents elicited by pH jumps (pH 7 to 4) are shown. (C) The influence of anionic phospholipid on KcsA inactivation. K+ currents were recorded from macropatches of WT KcsA reconstituted in plain asolectin lipids (WT), asolectin lipids with an added 25% of egg PA (WT + 25% PA) or asolectin lipids with an added 50% of egg PA (WT + 50% PA). (D) Effects of R64A, R64L, R89A and R64,89A KcsA mutations on channel inactivation upon reconstitution in plain asolectin lipids. The holding potential was set to +150 mV in all these experiments.