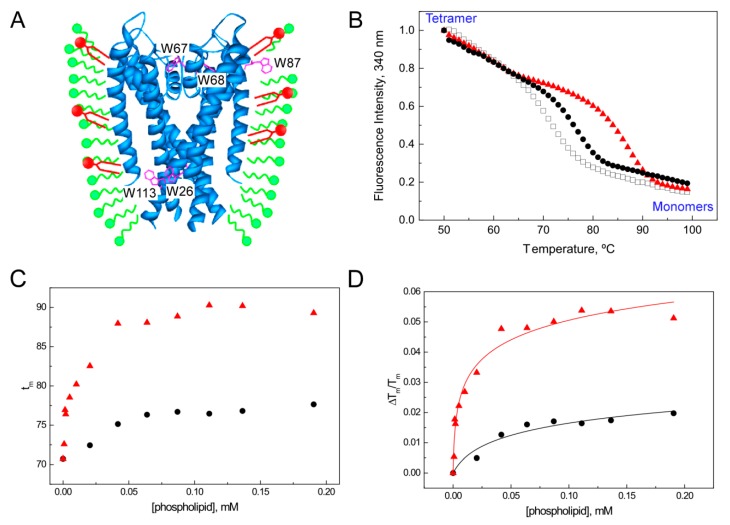
Figure 3.
Binding of lipids to KcsA followed by the protein thermal denaturation assay. (A) Scheme of the mixed-micelles system, where both lipids (small amounts, in red) and protein are completely solubilized by an excess of detergent (in green). The intrinsic fluorescence from the five Trp residues highlighted in magenta can be used to monitor the thermal denaturation of KcsA. (B) Typical thermal denaturation profile of DDM-solubilized KcsA, where the dissociation of the native tetramer follows a sigmoidal behavior. Addition of 0.1 mM of DOPC (black dots) or DOPA (red triangles) results in an increase of the stability of the protein in plain micelles (white squares). (C) Dependence of the thermal stability of KcsA WT on phospholipid concentration. Experiments were performed at 0.5 µM protein concentration in 20 mM HEPES (pH 7.0), 1 mM DDM, 100 mM NaCl, increasing the amounts of DOPC or DOPA. (D) Solid lines represent the best fits of the experimental data points to the ligand binding model described in Equation (4). The estimated dissociation constants (KD) for the single set of binding sites detected in these experiments are 9 ± 6 µM and 0.5 ± 0.2 µM for DOPC and DOPA, respectively.