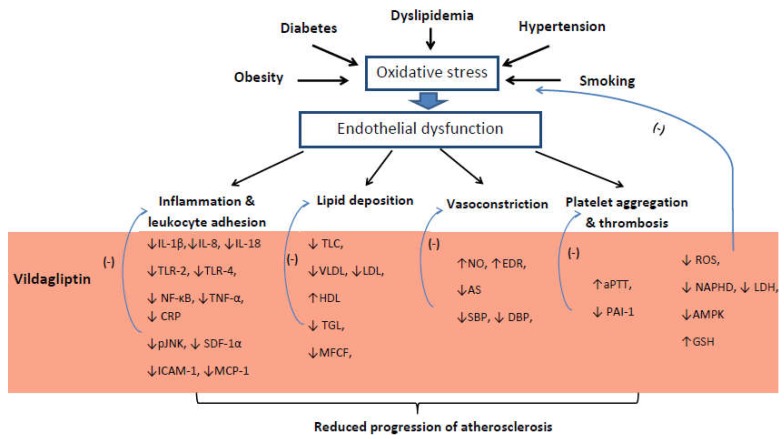
Figure 1.
Proposed influence of vildagliptin on atherosclerosis pathophysiology. Note: ↓ = reduction, ↑ = increase, (-) = inhibition, IL-1β = Interleukin 1 beta, IL-8 = Interleukin 8, IL-18 = Interleukin 18, TLR2 = Toll-like receptor 2, TLR4 = Toll-like receptor 4, NF-κB = nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, TNF-α = tumor necrosis factor α, CRP = C-reactive protein, pJNK = phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal kinase, SDF-1α = stromal cell-derived factor 1, ICAM-1 = intercellular adhesion molecule 1, MCP-1 = Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, TLC = total cholesterol level, VLDL = very low density lipoprotein, LDL = low density lipoprotein, HDL = high density lipoprotein, TGC = triglycerides, MFCF = macrophages foam cells formation, NO = nitric oxide, EDR = endothelial-dependent relaxation, AS – arterial stiffness, SBP = systolic blood pressure, DBP = diastolic blood pressure, aPTT = activated partial thromboplastin time, PAI-1 = plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, ROS = reactive oxygen species, NADPH = Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, LDH = lactate dehydrogenase, AMPK = 5’AMP-activated protein kinase, GSH = glutathione.