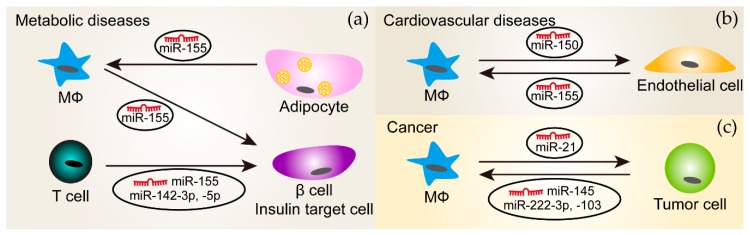
Figure 2.
The delivery of miRNAs between immune cells and the other cell types through extracellular vesicles (EVs) in diseases. (a) In metabolic diseases (such as obesity and diabetes), miR-155 is transported from macrophages (MΦ) and T cells to β cells and insulin target cell types, respectively, which was shown to affect glucose metabolism. Moreover, EVs derived from adipocytes that are from obese mice contain miR-155 and carry this miRNA to macrophages. miR-142-3p and -5p are also packaged in EVs secreted from T cells and mediate the crosstalk between T cells and insulin target cells; (b) In cardiovascular diseases, macrophages and endothelial cells communicate with each other through miR-150 and miR-155 enriched in their EVs, respectively; (c) In cancers, tumor cells could secret EVs that transport miR-145, -222-3p or -103 to macrophages. Conversely, tumors cells receive miR-21 from macrophages through EVs. The arrows indicate the direction of EV transfer.