Figure 1.
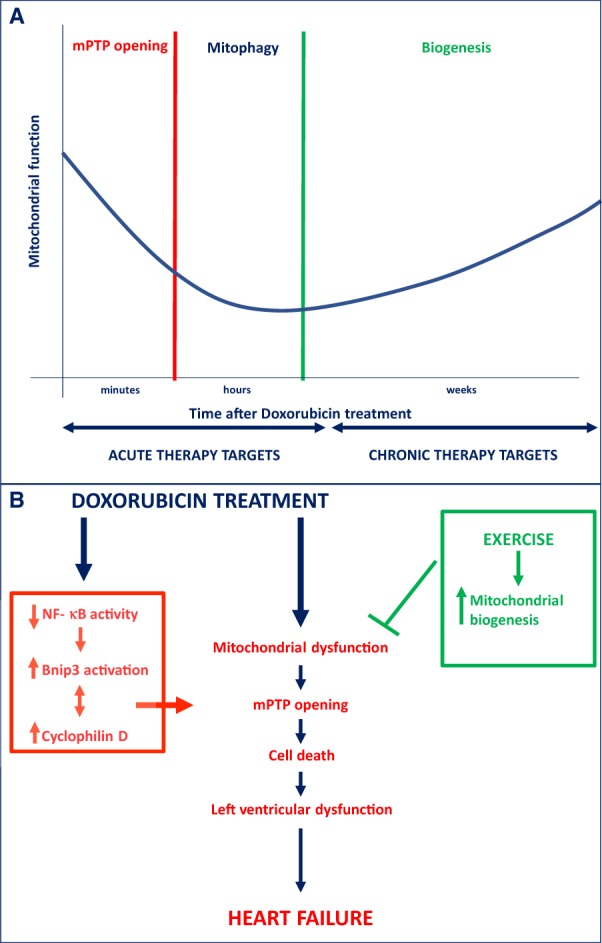
(A) Staged approach of potential mitochondrial targets to attenuate Dox-induced cardiotoxicity, ranging from acute to more chronic stages after Dox administration. (B) Underlying mitochondrial and cell death mechanisms leading to Dox-induced cardiotoxicity. Bnip3, Bcl-2/19 kDa interacting protein 3; mPTP, mitochondrial permeability transition pore; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB.
