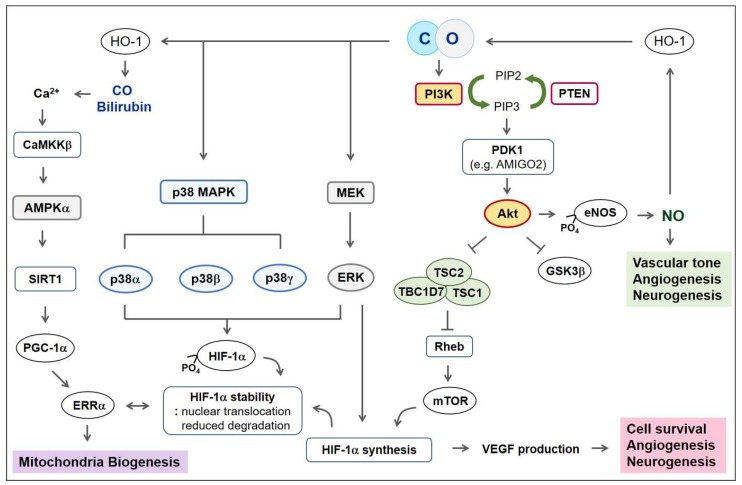
Figure 2.
Schematic figures showing various signaling molecules influenced by the CO-HO-1 pathway. Firstly, CO can activate PI3K-Akt-eNOS-NO signaling. CO/NO crosstalk can lead to vessel dilation, angiogenesis and neurogenesis. NO-mediated HO-1 induction can produce CO, forming a positive feedback loop. Akt also inactivates GSK3β and the TBC1D7/TSC1/TSC2 complex. Then, activation of mTOR through inhibition of Rheb results in protein translation, such as HIF-1α. HIF-1α-mediated VEGF production and secretion induce cell survival, angiogenesis and neurogenesis. Secondly, through phosphorylation of HIF-1α by p38 MAPK and ERK, CO may stabilize HIF-1α resulting in its nuclear translocation and upregulation of ERRα expression. Thirdly, the combination of CO and bilirubin among HO-1 metabolites may initiate Ca2+ entry, consequently stimulating CaMKKβ-mediated AMPKα activation. AMPKα activates SIRT1, leading to PGC-1α deacetylation and de-ubiquitination. Stabilized PGC-1α upregulates ERRα, which are critical for mitochondrial biogenesis. Abbreviations: CO, carbon monoxide; HO, heme oxygenase; NO, nitric oxide; eNOS, endothelial NO synthase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; TSC1, hamartin; TSC2, tuberin; TBC1D7, tuberin Tre2-Bub2-Cdc16 domain family member 7; HIF-1α, Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK, extracellular-signal-related kinase; AMPKα, adenosine monophosphate kinase α; ERRα, estrogen-related receptor α; CaMKKβ, Ca2+-calmodulin kinase kinase β; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-coactivator-1α.