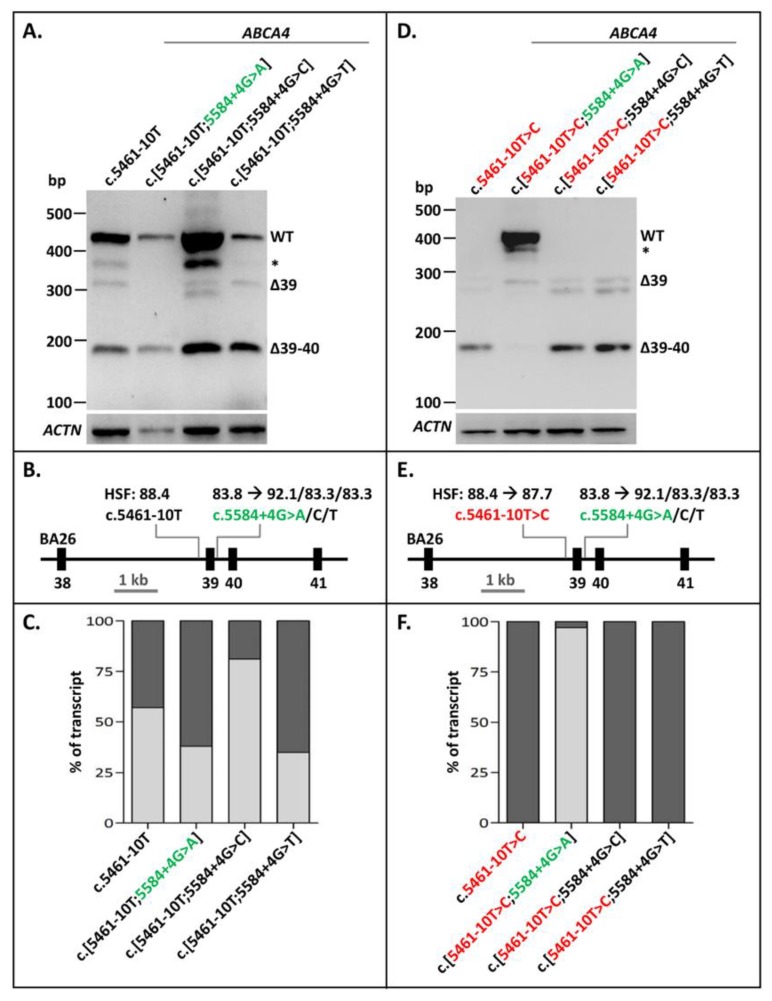
Figure 1.
Rescue of Exon 39/40 skipping due to ABCA4 variant c.5461-10T>C by 5′-splice-site strengthening. (A) The effect of altered nucleotides at Position c.5584+4 in the WT BA26 construct. None of the variants had a significant effect on Exon 39/40 splicing. Natural skipping of Exons 39/40 was observed for all. (B) Schematic overview of the BA26 construct used in A annotated with the Human Splicing Finder (HSF) scores with a range of [0–100], of which a higher score indicates a stronger splice prediction. (C) Semi-quantification of the ratio of correctly (light gray rectangles) and aberrantly spliced (dark gray rectangles) RT-PCR products due to altered nucleotides at Position c.5584+4 in the WT BA26 constructs. When multiple aberrant products were observed, the percentages were summed up. (D) The effects of altered nucleotides at c.5584+4 in the BA26 construct containing the c.5461-10T>C variant were that c.5584+4G>A, but not +4G>C or +4G>T, rescued the exon skipping due to c.5461-10T>C. (E) Schematic overview of the BA26 construct used in B. (F) Semi-quantification of the ratio of correctly (light gray rectangles) and aberrantly spliced (dark gray rectangles) RT-PCR products in BA26 construct containing c.5461-10T>C alone and together with rescue variants. * Band was identified as heteroduplex by Sanger sequencing. Red lettering indicates pathogenic variant. Green lettering indicates variant that rescued exon skipping.