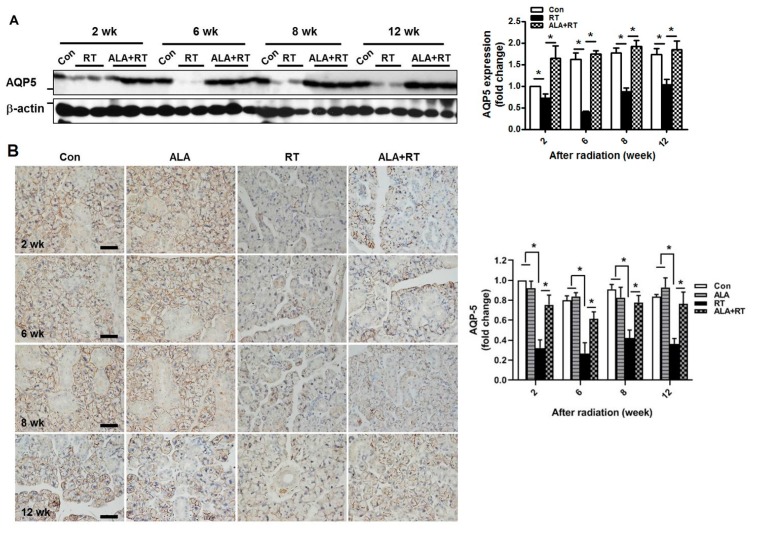
Figure 2.
The administration of ALA improves radiation-induced AQP5 expression. Sprague–Dawley rats were subjected to 18 Gy radiation in the head and neck region. (A) SGs were collected at each time points after irradiation and subjected to Western blotting. β-actin was used as the loading control. Western blot for the expression of AQP5 is normalized to β-actin, the expression was shown as signal intensity, and the expression in each group was represented as fold change. The fold change is calculated as the ratio of the final value in each group to the value in the control group at 2 weeks (set as “1”). Size markers mean 25 and 50 kDa from upper. Con; control (n = 3). RT; irradiation only group (n = 4). ALA+RT; ALA plus irradiation groups (n = 3). (B) immunohistochemical staining of AQP5 was shown in representative images. Positive signals were calculated as signal density. The fold change is calculated as the ratio of the final value in each group to the value in control group at 2 weeks (set as “1”). Scale bar, 50 μm. N = 3-4 SGs/group. Values are represented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05.