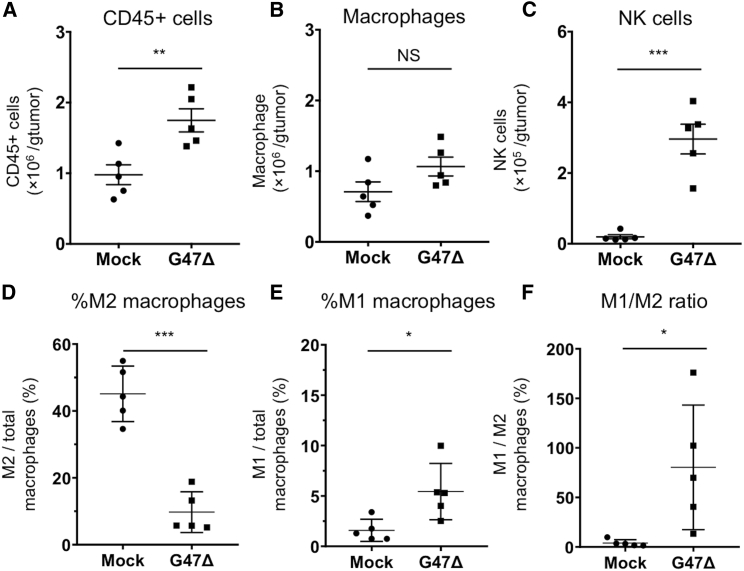
Figure 6.
Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in MKN45 Subcutaneous Tumors Treated with G47Δ
Athymic mice bearing MKN45 subcutaneous tumors were inoculated intratumorally with G47Δ (1 × 106 PFU) or mock. Tumor tissues were harvested 2 days after these treatments. After removal of debris and doublets, tumor-infiltrating cells were stained with CD45-Brilliant Violet (BV)785, CD11b-BV605, F4/80-APC, CD86-PE/Cy7, CD206-PE, and CD49b-FITC, followed by flow cytometric analysis. For all channels, positive and negative cells were gated on the basis of fluorescence minus one controls, and CD86 and CD206 were gated with appropriate isotype controls. (A–F) Absolute numbers of CD45+ cells/g of tumor (A), absolute numbers of macrophages (CD45+CD11b+F4/80+)/g of tumor (B), absolute numbers of NK cells (CD45+CD49b+)/g of tumor (C), the ratio of M2 macrophages (CD206+CD86− macrophages) to total macrophages (D), the ratio of M1 macrophages (CD206−CD86+ macrophages) to total macrophages (E), and the ratio of M1 macrophages to M2 macrophages (F) were compared between the two treatment groups. Bar represents mean ± SEM (n = 5). A Student’s t test was used to determine the statistical significance (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; NS, not significant).