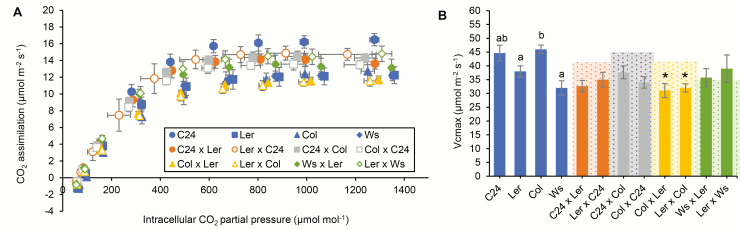
Fig. 2.
The CO2 gas exchange of 3-week-old hybrids compared with parents. The plants were sown on MS solid medium before being transferred into soil at 10 d old. Plants were grown under a light cycle of 16 h/8 h, in a light intensity of 120 µmol photons m−2s−1, at 21 °C. (A) The net CO2 assimilation rate of the hybrids and parents was measured under an increasing partial pressure of atmospheric CO2 under a saturating irradiance at 1000 µmol m−2 s−1 using a gas exchange analyser (LI-6400XT, LICOR). The x-axis shows the intercellular CO2 partial pressure. The analyses were carried out on the largest leaf on the rosette of each plant measured. Each data point represents the average and SE of n≥3. (B) Comparison of the maximum rate of Rubisco carboxylation (Vcmax) between hybrids and the parents. The curve fitting result using the dataset from (A). The curve fitting was carried out by fitting the dataset from (A) to the C3 photosynthesis model (Farquhar et al., 1980). Each data point represents the average and SE of n=3. Different letters above the columns represent a significant difference between the parents (ANOVA, P<0.05). Asterisks represent significant differences between the hybrid and the better parent (ANOVA, P<0.05). No significant differences were found between hybrids and the lower parents, and between the hybrids and the growth under the average value of the parents (indicated by red dashed lines; ANOVA, P>0.05).