Figure 2.
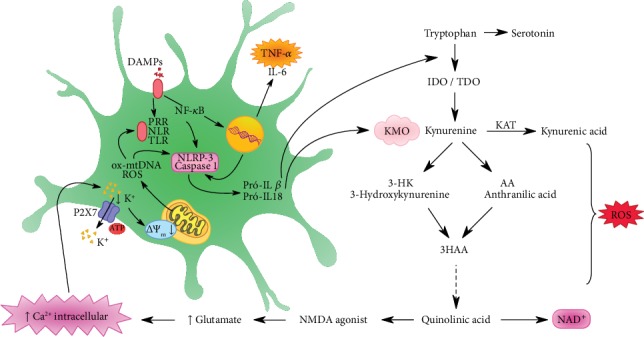
Danger-Associated Molecular Pattern (DAMP) binds to the Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) expressed on the cytosol or in innate immune cell membranes. The cascade triggered by these PRRs leads to NLRP3 inflammasome and caspase-1 activation, which can activate IL-1β and IL-18. Oxidized mitochondrial DNA (ox-mtDNA) and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) also activate the inflammasome. NF-κB, through the transcriptional activation pathway, generates tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18 activate the enzymes IDO and TDO of the kynurenine pathway, degrading tryptophan into kynurenine. These two cytokines further activate KMO, which is the enzyme that directs kynurenine to be degraded to 3HK and quinolinic acid, both neurotoxic agents, over the kynurenic acid, a neuroprotective agent. Kynurenic acid is an NMDA receptor agonist and increases glutamate levels and consequently intracellular calcium. Excessive amounts of ROS are produced over the kynurenine pathway.
