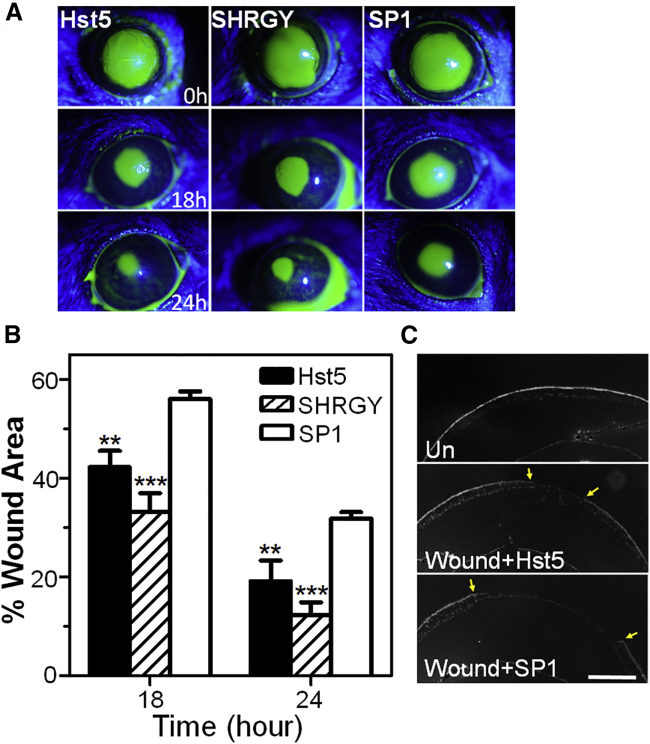
Figure 8.
Application of Histatin-5 or SHRGY Peptides Accelerates Corneal Wound Closure Rates in a Murine Corneal Epithelial Injury Model
(A) Slit-lamp biomicroscopic images of murine corneas using a cobalt filter and fluorescein dye staining of the wounded areas are shown among the experimental groups (n = 7 for each group) (Hst5 [80 μM], SHRGY [80 μM], or SP1 [80 μM]). (B) Wound areas at multiple time points were measured using ImageJ software. Measurement of percentage remaining corneal wound area at 18 and 24 h compared to baseline showed statistically significant improvement in Hst5 and SHRGY groups compared to SP1. (C) DAPI stained cross-sections of the murine cornea and anterior segment of the eye show the reduction in size of the epithelial wound at 24 h in Hst5-treated mice compared with SP1 control mice. Wounded area is shown by arrowheads. Scale bar, 500 μm. Statistical significance was determined by a two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. % Wound area = (wound area at time x/wound area at time 0) × 100.