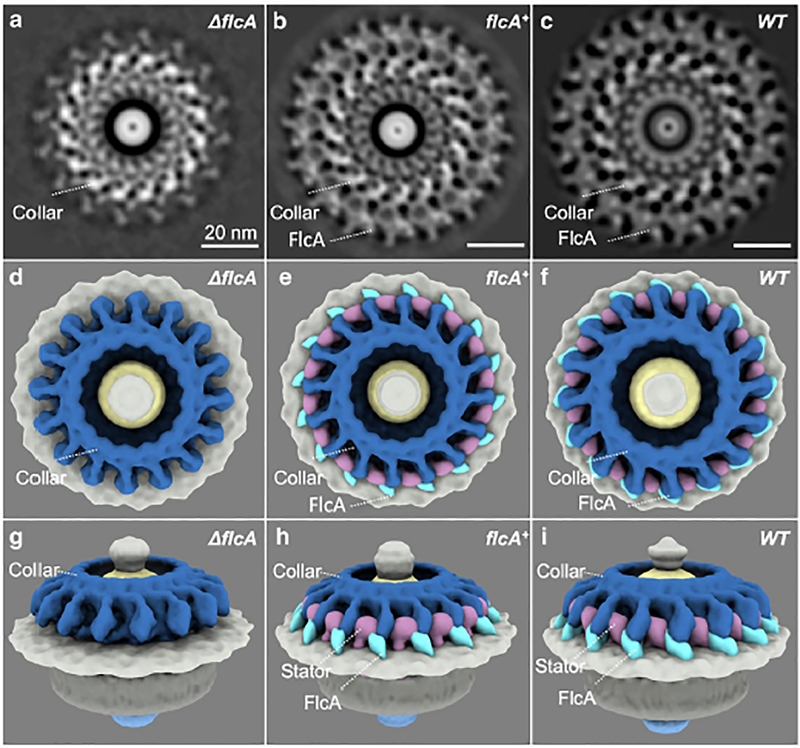
Figure 3. Structures of the flagellar motor from ΔflcA, flcA+ and WT cells.
(A—C) A section of the subtomogram average of the Δbb0326 or ΔflcA, bb0326+ or flcA+ and WT motors, respectively. (D—F) A top view of the 3D rendering of the ΔflcA, flcA+, and WT motors, respectively. (G—I) Side views of the ΔflcA, flcA+, and WT motors, respectively. The core port of the collar is colored in steel blue. The gene products of flcA are colored in cyan. The stator complex is colored in plum. Note that the in flcA+ cells, the collar and other structures appear to be slightly different from the wild-type cells (B, C) likely due to the overexpression of flcA from the multicopy shuttle vector used to complement the mutant.