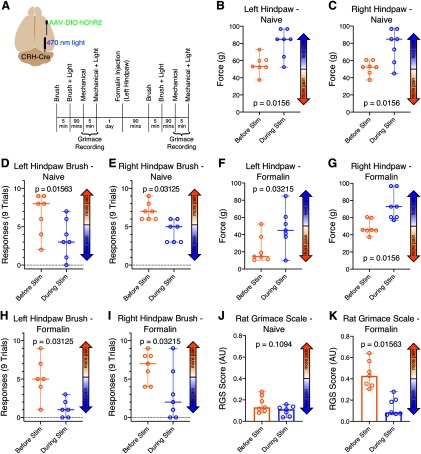
Figure 9.
Optogenetically activating a subset of GABAergic CeA-LPB axon terminals in CRH-Cre rats suppresses pain in naive animals, as well as during acute formalin pain. A, Locations of viral construct injection, fiberoptic implantation, and experimental design. B–K, Data are medians and 95% CIs. Selectively activating CRH CeA terminals in LPB increased mechanical withdrawal thresholds in both hindpaws (B, C) and decreased mechanical allodynia responses (D, E), but did not affect spontaneous pain RGS scores (J) in the naive animal. During acute formalin pain, optogenetically activating this subset of CeA-LPB axon terminals also increased hindpaw mechanical withdrawal thresholds (F, G) and decreased both mechanical allodynia responses (H, I) as well as RGS scores (K).