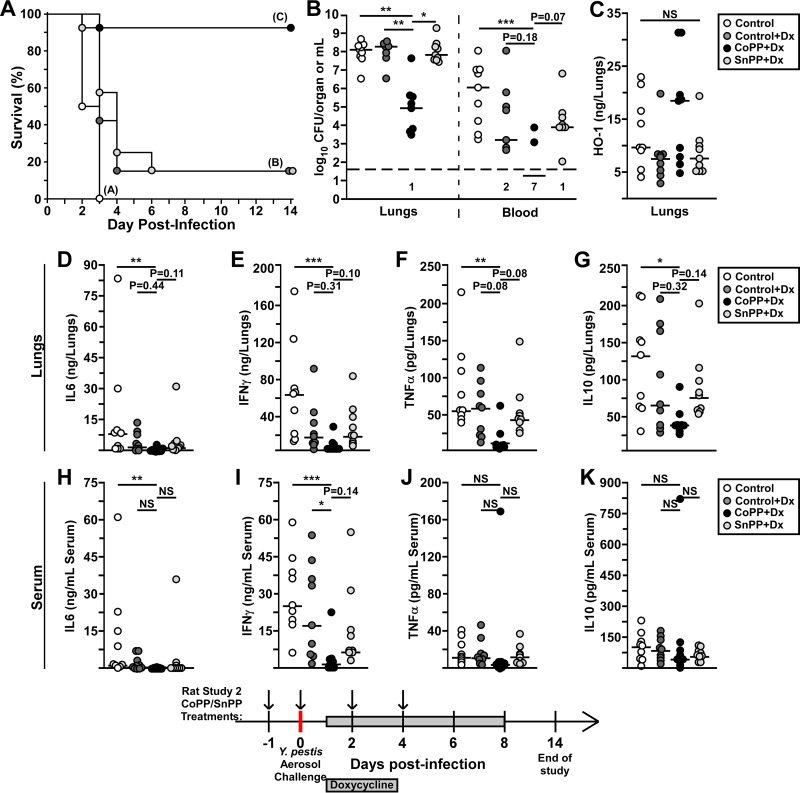
FIG 6.
Stimulation of HO-1 enhances doxycycline efficacy in preventing bacterial growth. Groups of 28 (n = 7 per group) male SD rats were challenged by inhalation exposure to Y. pestis CO92 (individual doses shown in Table S3 in the supplemental material). For the study design, the rats were pretreated with 5 mg/kg CoPP (CoPP+Dx) or SnPP (SnPP+Dx) i.p. on days −1, 0, +2, and +4. Doxycycline (Dx) treatment (20 mg/kg IG) began 24 hpi and continued once daily for 7 days. Vehicle control animals received PBS by i.p. injection and water by oral gavage (control). (A) For each group, four rats were monitored for survival over 14 days. (B to L) The remaining three rats per group were euthanized at 48 hpi. The lungs (B to G) and blood (B, H to K) were removed and processed for CFU (B), HO-1 (C), IL-6 (D and H), IFN-γ (E and I), TNF-α (F and J), and IL-10 (G and K). The data shown were collected in three independent trials (n = 9 to 12 per group). The bars indicate median values. Data were pooled for statistical analyses by the Gehan-Breslow log rank (A) or Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple-comparison test (B to K). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; NS, not significant. LH, lung homogenate.